Do you ever experience difficulty bending forward due to lower back pain? Have you noticed that you feel stiffness and pain in your lower back when you stand up after long periods of sitting? Are you looking for ways to strengthen your lower back at home? Then you should read this blog.
Here will guide you through a series of simple yet effective exercises for the lower back that include strengthening and stretching exercises.
These exercises will not only make your lower back feel better, but they will also protect it from future injuries. The best part? You can perform them conveniently within the confines of your own home, making them easily accessible and adaptable to your busy schedule.

- Importance of a Strong Lower Back
- 1. Spinal Stability
- 2. Pain Prevention
- 3. Core Strength and Balance
- 4. Pain Free Life
- 5. Proper Functional Movement
- 6. Enhanced Athletic Performance
- Anatomy of Lower Back
- 12 Best Exercises for Lower Back Strength
- 1. Superman
- How To Do It
- Tips
- 2. Hip Bridge
- How To Do It
- Tips
- 3. Good Morning
- How To Do It
- Tips
- 4. Plank
- How To Do It
- Tips
- 5. Side Plank
- How To Do It
- Tips
- 6. Bird Dog
- How To Do It
- Tips
- 7. Lying Bent-Knee Twist
- How To Do It
- Tips
- 8. Deadlift
- How To Do It
- Tips
- 9. Cat-Cow
- How To Do It
- Tips
- 10. Flat Bench Hyperextension
- How To Do It
- Tips
- 11. Lying Straight Leg Raise
- How To Do It
- Tips
- 12. Dumbbell Side Bend
- How To Do It
- Tips
- Strengthen Your Back Safely
- Tips and Technique To Lower Back Workout
- Warnings
- Additional tips for managing lower back pain
- 1. Maintain good posture
- 2. Take breaks from prolonged sitting
- 3. Use proper lifting techniques
- 4. Maintain a healthy weight
- 5. Practice stress management techniques
- FAQs
- Can I strengthen my lower back at home without any equipment?
- Can yoga help strengthen my lower back?
- Can I do lower back exercises if I have a herniated disc?
- Takeaway
- Disclaimer:
- References
- Bodyweight Back Workout at Home Without Equipment
Importance of a Strong Lower Back
Wouldn’t it be great if you could lift your child or even a bag of groceries without as much effort? If you answered “yes” to any of the above, you might benefit from workouts that help strengthen and improve the flexibility of your lower back.
The importance of a strong lower back cannot be overstated when it comes to overall health and well-being. Here are some key reasons why developing strength in this area is crucial:
The stronger your low back is, the better your posture, athletic performance, and mobility. You will be less likely to suffer from back pain.
1. Spinal Stability
The back, or lumbar spine, is crucial for supporting the weight of the upper body and ensuring proper alignment. A strong lower back provides stability and prevents excessive strain on the spine.
This stability is essential for maintaining good posture and reducing the risk of injuries, such as herniated discs or muscle strains.
2. Pain Prevention
Lower back pain is a prevalent issue that affects millions of people worldwide. Weakness in the muscles surrounding the lower back can contribute to pain and discomfort.
Studies have shown that doing exercises to strengthen the lower back muscles can help relieve existing pain and prevent future occurrences by providing better support and stability to the spine.
3. Core Strength and Balance
The lower back is an integral part of the core musculature, which includes the abdominals, obliques, and pelvic floor muscles. Strengthen the entire core for more stable movements and ultimately less pain. It also improves posture and contributes to a more aesthetically pleasing physique.
4. Pain Free Life
The strength of the lower back acts as a protective mechanism against injuries during physical activities and everyday movements.
Whether you’re lifting heavy objects, participating in sports, or performing household chores, having a solid foundation of lower back strength reduces the risk of strains, sprains, and other musculoskeletal injuries.
5. Proper Functional Movement
It’s important to have strong lower back muscles for doing things like bending, twisting, and lifting.
When you are engaged in recreational activities or carrying out daily tasks, a well-conditioned lower back enables you to move with greater ease, efficiency, and reduced risk of injury.
6. Enhanced Athletic Performance
Athletes and fitness enthusiasts can significantly benefit from a strong lower back. It provides a solid foundation for explosive movements, such as jumping, running, and throwing.
A strong back also boosts overall body strength and power, allowing athletes to shine and lessen the chance of sporting mishaps.
Anatomy of Lower Back
Understanding the anatomy of the lower back is essential for comprehending its function and addressing related issues effectively.
The back consists of several layers of muscle, stacked like a sandwich. The muscles of the back subdivide into three categories.
- The upper back is made up of a large triangular-shaped muscle called the trapezius.
- The middle back consists of the latissimus dorsi.
- The lower back is made up of the erector spine muscles.
The lower back, also known as the lumbar spine, is a complex structure that plays a crucial role in supporting the upper body and facilitating movement.
Here are the key components of the lower back anatomy:
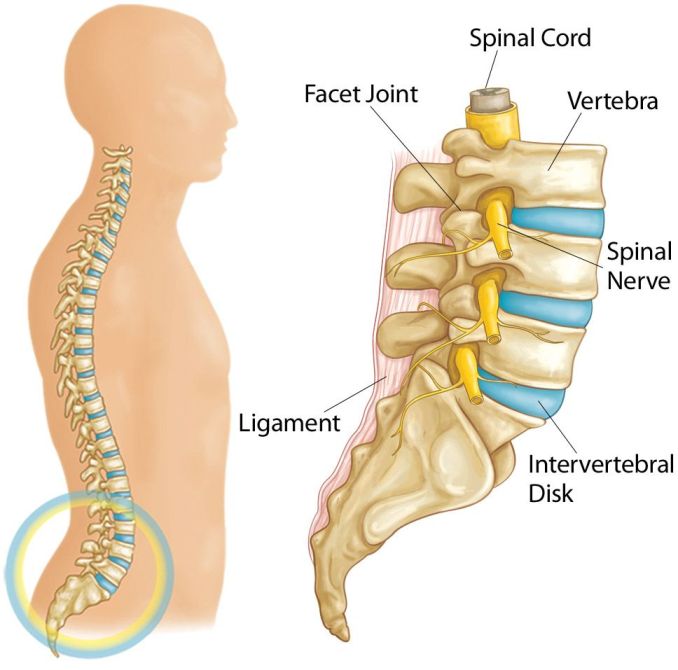
- Vertebrae: The lumbar spine consists of five large vertebrae (L1 to L5) that support the weight of the upper body.
- Intervertebral Discs: These discs, located between adjacent vertebrae, act as shock absorbers and provide flexibility to the spine.
- Spinal Joints: Facet joints connect the vertebrae, allowing for movement and providing stability in the lower back.
- Spinal Cord and Nerves: The spinal cord runs through the spinal canal formed by the vertebrae, and nerve roots branch out to various parts of the body, facilitating communication with the brain.
- Muscles: Key muscles of the lower back include the erector spinae group.
- Ligaments: Ligaments in the lower back, such as the anterior and posterior longitudinal ligaments, and interspinous ligaments, provide stability by connecting the vertebrae.
12 Best Exercises for Lower Back Strength
We know that having a strong and healthy back is very important because it helps support your body and keep your posture good. That’s why we have carefully curated a list of exercises that target the lower back muscles, helping you build strength, flexibility, and stability.
This workout routine includes the best exercises for strengthening and building muscle in your upper and lower back, both for your superficial muscles (those closer to the skin) and your deep muscles (those closer to bone and internal organs).
These back exercises also strengthen the glutes, hamstring, quadriceps, obliques, Rectus abdominis.
Now, let’s talk about the best exercises for strengthening your lower back and improving your posture. You can use different types of fitness equipment and do some exercises with your own body weight at home.
- Superman
- Hip Bridge
- Good Morning
- Plank
- Side Plank
- Bird Dog
- Lying Bent-Knee Twist
- Deadlift
- Cat-Cow
- Flat Bench Hyperextension
- Lying Straight Leg Raise
- Dumbbell Side Bend
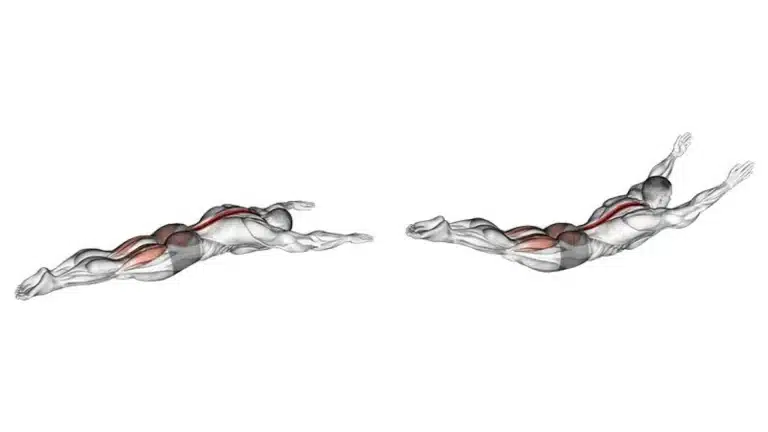
1. Superman
Superman is an effective exercise for strengthening the muscles of the lower back, core, and glutes. If done regularly, the Superman exercise may help alleviate back pain that is related to weak back muscles.
The primary focus of the superman exercise is to target and strengthen the erector spinae muscles in the lower back.
In addition, to strengthening lower back muscles, it also works on your glutes and your hamstring muscles.
How To Do It
- Lay with your stomach flat on the ground.
- Extend your arms in front of you, with your palms facing down.
- Lift your head and raise your arms and your chest off the ground as far as possible.
- Bend your legs and lift your thighs off the ground, as much as possible. (Try to make a big “U” with your back.)
- Hold the lifted position for a few seconds while engaging the target muscles.
- Slowly lower your arms and legs back to the starting position.
- Repeat for the desired number of repetitions.
Tips
- For your first few workouts, try holding for only 5 or 10 seconds, and then work your way up to 30 seconds over time.
- Do not hold your breath. Breathe regularly.
- Start with a comfortable range of motion.
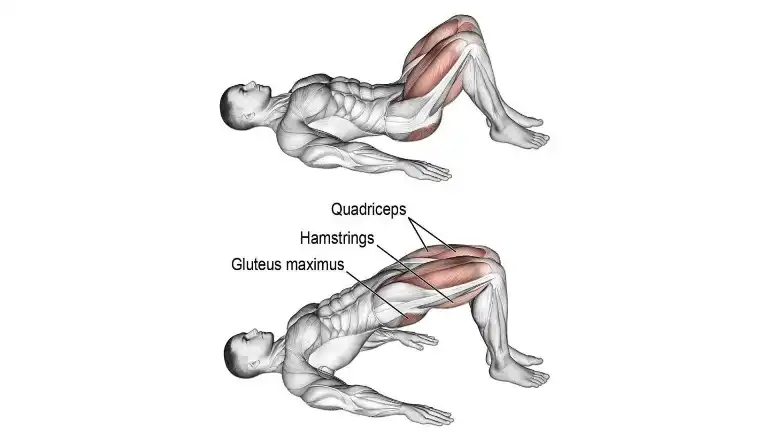
2. Hip Bridge
The hip bridge is a good starter move for butt, hamstring, and low back muscles. It is the best exercise to manage chronic lower back pain.
When you sit for most of the day, your glute muscles can become weaker and the hip flexors in the front of your thighs can become shorter, making them feel tight.
But when you practice glute bridges regularly you are targeting your glutes and your lower back muscles, those muscles that are meant to hold your body upright will get stronger.
How To Do It
- Lie down on the floor with your knees bent and your feet flat on the ground.
- Keep your arms at your side with your palms down.
- Lift your hips off the ground until your knees, hips, and shoulders form a straight line.
- Squeeze your glutes hard and keep your abs drawn in to avoid overextending your back during the exercise.
- Hold your bridged position for a couple of seconds before easing back down.
Tips
- Don’t overextend your back during the exercises, this may cause lower back pain.
- To make it more challenging, hold a weight plate on your lap.
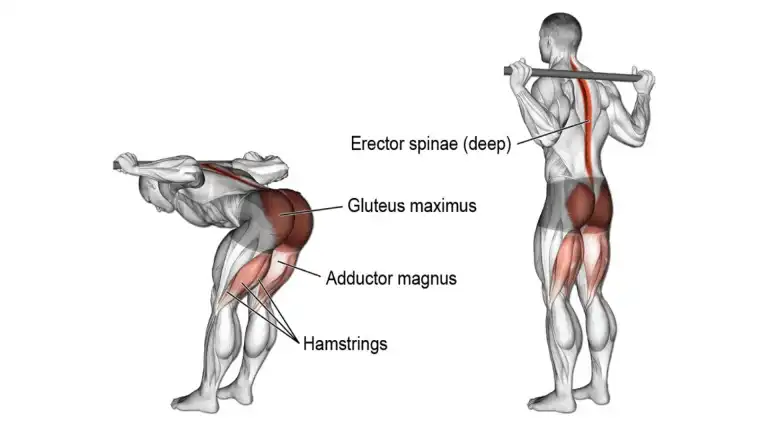
3. Good Morning
Good Morning is a compound exercise that primarily targets the muscles of the posterior chain, including the hamstrings, glutes, and lower back
When done with solid spinal alignment and perfect form, the good morning is one of the best exercises that can be a great move for improving your back health and alleviating your lower back pain.
To allow your lower back to get used to the good morning exercise, start with bodyweight or a stick and add more weight slowly.
How To Do It
- Stand holding a stick on the back of your shoulders, grasping the stick at each side.
- Keeping your knees slightly flexed and your back and neck neutral.
- Slowly hinge forward at the hips while maintaining a slight bend in your knees.
- Lower your torso until you feel a stretch in your hamstrings.
- Keep your weight on your heels and avoid rounding your back or letting your knees collapse inward.
- Pause at the bottom position, and then return to the starting position by driving through your hips and engaging your hamstrings and glutes.
- Repeat for the desired number of repetitions.
Tips
- Keep your back and neck neutral throughout the exercise.
- Start with light weights or no weights at all.
- It is recommended that the lifter avoid rounding (flexing), or rotation (twisting) at any point during the movement.
4. Plank
The Plank is a popular core-strengthening exercise that targets multiple muscles, including the abdominals, back, and stabilizing muscles.
It is an isometric exercise where you hold a position similar to the top of a push-up, with the body’s weight borne on forearms, elbows, and toes.
Although the focus is on the core, the Plank also engages other muscle groups, including the shoulders, glutes, and legs. It contributes to better posture, reducing the risk of back pain and promoting proper alignment.

How To Do It
- Position yourself face down on the floor with your forearms on the ground and elbows directly beneath your shoulders.
- Engage your core by drawing your navel toward your spine and squeezing your glutes.
- Your body should form a straight line from your shoulders to your ankles.
- Maintain a neutral neck position, looking down at the floor to avoid straining your neck.
- Hold the position for a specific duration, starting with 20-30 seconds and gradually increasing as you build strength and endurance.
- To get out of the Plank, lower your knees to the ground and rest.
Tips
- Do not let your lower back sag or your butt rise. Ensure your body is straight and rigid.
- Keep your glutes and core muscles contracted.
- Your neck should be in line with your body, not tilted up, which could strain the neck.
Know More: Plank Exercise: Benefits, Variations, Muscles Worked, Tips
5. Side Plank
Side Plank is a core-strengthening exercise that primarily targets the oblique muscles, but also engages the entire core and stabilizing muscles.
The exercise activates the entire core, including the deep abdominal muscles (transverse abdominis) and the muscles of the lower back, promoting overall core stability and strength.
If you find the exercise challenging, modify it by bending your knees and resting on your bottom knee instead of your feet.

How To Do It
- Lie on your left side on the floor, with your right foot on top of your left foot and your right arm resting on your side.
- Raise your body by placing your left forearm flat on the floor so that it’s perpendicular to your torso.
- Lift your torso until your left upper arm is straight underneath you, with your elbow bent 90 degrees and your forearm flat on the floor.
- In this position, only your left forearm making contact with the floor and your body forms a diagonal line that is at about a 20-degree angle to the floor.
- Keep your abs pulled in tight and hold this position for as long as you can, and then repeat on the left side.
Tips
- Keep your legs and body straight.
- Avoid letting your hips sag during exercises.
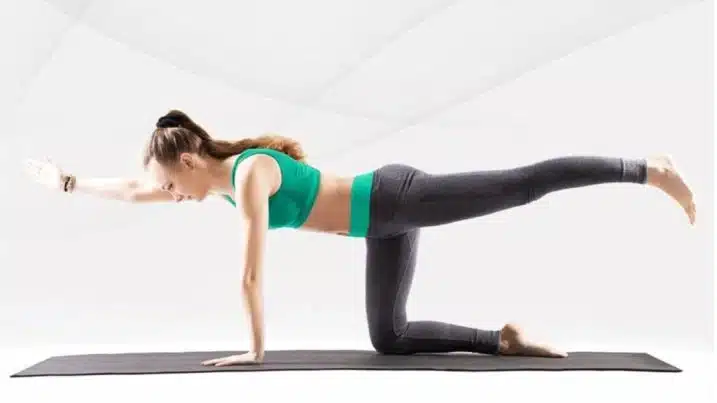
6. Bird Dog
The bird dog is an exercise that looks elegant and is also very effective for training the abdominal muscles and lower back muscles. Several other muscles are also addressed, including the glutes.
The bird dog is a real stability exercise that ensures a stable trunk. It owes its name to the position which alternates between sitting on hands and knees (dog) and stretching the arms and legs (bird).
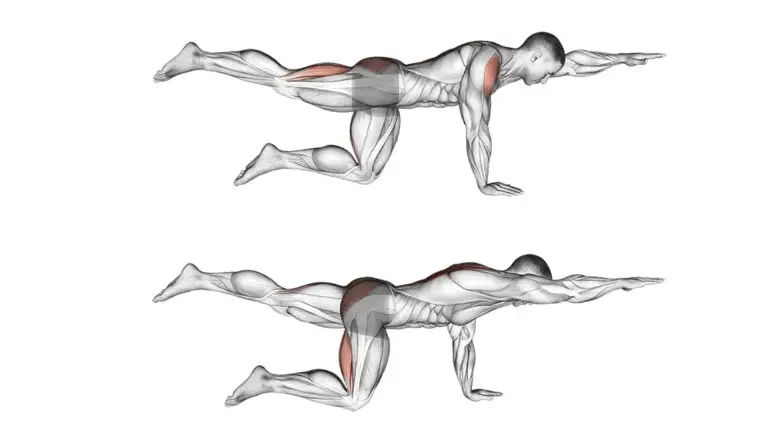
How To Do It
- Get on your knees and place your hands on the floor in front of your body at shoulder width.
- Contract your abs and lift one hand and the opposite knee slightly off the floor.
- You are now balancing on the other hand and knee.
- Now extend your arm and leg all the way out. Try to form a straight plane from your hand to your foot.
- Hold this position for about 10 seconds and then return to the starting position.
- Repeat the exercise with the other side.
Tips
- This exercise gets harder when you perform the exercise on your toes instead of your knees.
- Don’t raise your leg and arm higher than your back.
Know More: 21 Bodyweight Shoulder Exercises: Beginner to Advance
7. Lying Bent-Knee Twist
The Lying Bent-Knee Twist, also known as the Supine Spinal Twist or Supine Twist, is a gentle stretching exercise that involves rotating the spine while lying on your back with bent knees.
It helps improve spinal mobility and flexibility by gently rotating the vertebrae, relieving tension and stiffness in the lower back.

How To Do It
- Lie on your back on the floor or mat with arms extended out to the sides to keep your body stable during the exercise.
- Raise and bent legs at a 90-degree angle, so thighs are vertical and lower legs are horizontal.
- Keeping your shoulders in contact with the floor, slowly lower your legs to one side until you feel a mild stretch in your lower back.
- Hold the stretch for 20-30 seconds while focusing on deep, relaxed breathing.
- Now, rotate your legs all the way to the right.
- Repeat for the desired number of reps.
Tips
- Maintain knee position throughout movement.
- Avoid forcing or overstretching.
- Keep your core tight during the movement to activate your obliques against resistance.
8. Deadlift
The Deadlift is a fundamental exercise that involves lifting a barbell or weight from the ground to a standing position. It mimics the motion of picking up a heavy object from the floor
The deadlift is the king of all exercises, and it is a powerful exercise designed to build an overall physique and strengthen the low back.
It is the best exercise for posterior chain muscle strengthening, especially for the erector spine, glutes, and hamstrings.
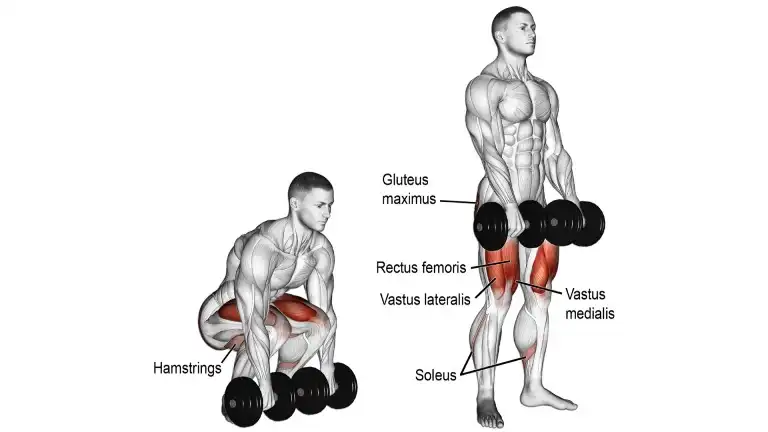
How To Do It
- Place a dumbbell in front of you. Grab the dumbbells in each of your hand.
- Remember to keep your back as straight as possible and contract your back and hamstrings.
- Raise the dumbbell from the ground using your hamstrings and glutes.
- Raise it to the point where your body is erect.
- Do not hyperextend your body as the weight shifts to the lumbar spine.
- Hold the dumbbell for a moment at the top of the lift and remember to the lockout.
- Now, lower the dumbbell slowly at a steady slow pace by bending at the hips first and then at the knees and let the weight touch the ground for a moment before you begin the next rep.
Tips
- Do not go through half of the exercise, complete the lift.
- If a deadlift is performed incorrectly, it can cause more harm than good. Keep the back straight at all costs.
- Avoid jerky movements and keep motion-controlled.
9. Cat-Cow
If back mobility is something you struggle with, then this is a great way to start. It will increase your chances of improving your back’s function and moving better.
The cat-cow exercise is a spinal mobilization exercise that helps a person “loosen” their spine. It improves movement of your lower back. It is a great way to mobilize your spine and the muscles responsible for extending it.
To do the cat-cow, the person is on their hands and knees and bends the spine up (like a cat) and then curves it downward (so your stomach hangs to the floor, like a cow)
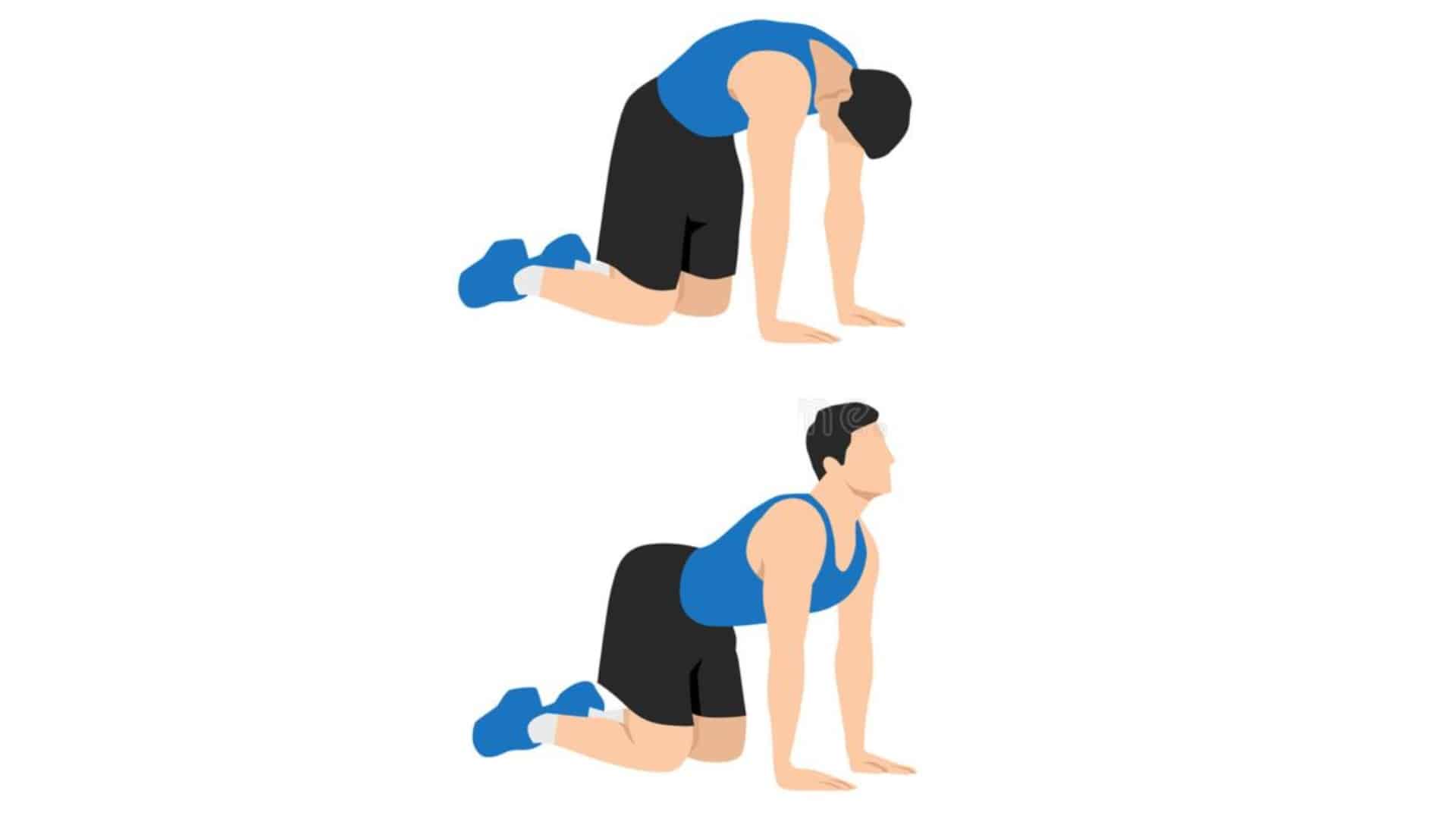
How To Do It
- Begin with your knees beneath your hips and your spine in a neutral position.
- Sink your back-down towards the floor and lift your head up at the same time, sticking your tailbone out to make a curve with your spine.
- Return to the initial position, and then tuck your head and tailbone in, arching through your spine as to mimic a camel hump. Take a big breath in at the same time.
- Move back and forth slowly, without pushing at either end of the movement.
Tips
- Aim to do these movements for 8-10 repetitions, to fully mobilize your lumbar spine or low back area.
- Move slowly and deliberately through the movement.
10. Flat Bench Hyperextension
Flat Bench Hyperextension exercise directly hits the erector spinae muscles, building a strong back.
You can also make hyperextensions more difficult by holding a plate to your chest or behind your head.
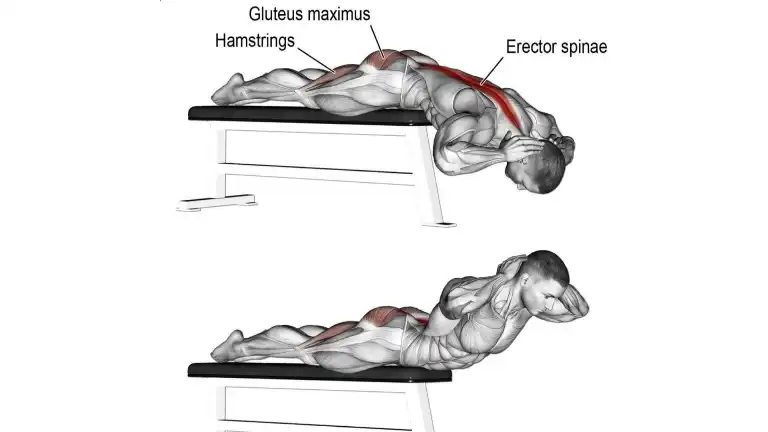
How To Do It
- Lie face down on a flat bench with your torso extending off the end, and hook your heels under the bench to prevent yourself from falling forward.
- Place your hands on your chest (or behind your neck) and bend down through your waist.
- Return to the start position, but avoid extending beyond the body level.
- Do the desired number of reps and sets.
Tips
- Avoid hyperextension beyond the body level.
- Keep movement always under control, without letting gravity take you down faster.
11. Lying Straight Leg Raise
Lying leg raises are touted as the best core exercise. But your hip flexors actually reap some major benefits of this move. So don’t be surprised if your hips feel a bit of the burn during this one.
It can also help alleviate low back pain since it improves the overall strength and stabilization of your core.
It is often used in Physical Therapy to help patients improve the strength of their lower extremities.
You need no special equipment to do a straight leg raise, apart from space where you can lie on your back freely.

How To Do It
- Lie face up on the floor/bench with your entire body straight and your hands at your sides to stabilize your torso.
- Hold your legs a few inches off the floor.
- Raise your legs up toward the ceiling until they are just short of perpendicular to the floor.
- Slowly lower your legs back to the starting position.
Tips
- Keep your lower back pressed against the bench or mat.
- Move slow and with control, making sure not to arch your back at any point in the move.
12. Dumbbell Side Bend
Dumbbell side bends are isolation exercises that target muscle groups on the side of your body—specifically the oblique muscles.
It is effective at targeting the internal and external obliques, strengthening the lateral flexion of your spine, improving spinal mobility, and helping to develop a strong and stable core.
It is a simple exercise that you can practice at home.

How To Do It
- Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart while holding a dumbbell with a neutral grip in your right hand with your arm hanging at your side.
- Bend sideways at the waist to the left as low as possible, using your oblique muscles to pull your torso down.
- Hold for a second and return to the starting position.
- You can complete the number of reps you want and repeat on the other side.
Tips
- Perform this exercise slow and steadily to work the obliques.
- Always keep your back straight, eyes facing forwards, and bend at the torso only.
Strengthen Your Back Safely
Strengthening the lower back should make you healthier and fitter while reducing pain. On the other hand, working out incorrectly can cause injury or worsen the pain. Before getting into a low back strength routine, keep safety in mind.
Tips and Technique To Lower Back Workout
Here is an exercise routine that strengthens your back.
- Always warm up your lower back before you start any exercises to increase blood flow and loosen up the muscles.
- Choose any 3-4 exercises you want to do and do 3-4 sets of 10-15 reps of each.
- You can either use a set of light weights or do each back exercise as a bodyweight exercise.
- Remember, the goal of this exercise is to complete it with proper form, while still challenging your body.
- Perform lower back exercises with slow and controlled movements.
- If you have any limitations or injuries, modify exercises to suit your needs.
- It is recommended to incorporate exercises that emphasize both the flexibility and strength of the lower back.
- If you have questions about a specific exercise or what would be best for you, consult a personal trainer or coach first.
- If you already have an exercise routine, you could try adding these exercises to help strengthen your lower back.
- After completing your back workout, spend a few minutes on a cool-down routine. Stretching the lower back and surrounding muscles can help prevent post-workout stiffness.
- Give your lower back muscles ample rest and recovery time between workouts.
Warnings
Always consult a doctor before beginning a new exercise program. For those experiencing persistent or strong pain in their backs, visit your healthcare provider or physical therapist before beginning a workout routine (even with a personal trainer).
If you experienced a traumatic injury such as a fall or accident, always seek medical help and further evaluation to rule out serious conditions.
If these exercises cause your back pain to increase, stop and seek medical help. Only work within your physical limits. Doing too much, or too fast, can increase back pain and slow the healing process.
Additional tips for managing lower back pain
In addition to these exercises, there are several other strategies you can incorporate into your daily routine to manage lower back pain effectively:
1. Maintain good posture
Practice proper posture throughout the day, whether you’re sitting, standing, or walking. Avoid slouching or hunching over, as this puts unnecessary strain on the lower back.
2. Take breaks from prolonged sitting
If you have a desk job or spend long hours sitting, make sure to take regular breaks to stretch and move around. Sitting for extended periods can contribute to lower back pain and muscle imbalances.
3. Use proper lifting techniques
When lifting heavy objects, bend your knees and use the strength of your legs rather than your back. Avoid twisting or jerking movements that can strain the lower back.
4. Maintain a healthy weight
Excess weight puts additional stress on the spine and can contribute to lower back pain. Maintain a healthy diet and engage in regular exercise to achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
5. Practice stress management techniques
Stress can contribute to muscle tension and exacerbate lower back pain. Incorporate stress-relief techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga into your daily routine.
FAQs
Can I strengthen my lower back at home without any equipment?
Yes, there are several lower back exercises that can be done without equipment. Bodyweight exercises like bridges, supermans, and bird dogs are effective for strengthening the lower back.
Can yoga help strengthen my lower back?
Yes, yoga can be beneficial for strengthening the lower back and improving flexibility. Poses like cat-cow, child’s pose, and sphinx pose target the lower back muscles. Consider incorporating yoga into your routine to enhance lower back strength.
Can I do lower back exercises if I have a herniated disc?
If you have a herniated disc or any pre-existing spinal condition, it’s essential to seek guidance from a healthcare professional or physical therapist. They can recommend specific exercises that are safe and appropriate for your condition.
Takeaway
These exercises are highly recommended for anyone interested in strengthening back muscles, and to improve posture. When you have perfect posture, you feel command, confidence, and less stress on your back when you have perfect posture.
Low Back strengthening exercises are an excellent way to prevent recurring back pain.
Increased stability, decreased chances of getting injured and improved function can be achieved by stronger core muscles.
Start incorporating these simple exercises into your daily routine and you will reap the benefits for a long time.
Disclaimer:
The information contained in this article is for educational and informational purposes only and is not intended as health advice.
We would ask you to consult a qualified professional or medical expert to gain additional knowledge before choosing to consume any product or perform any exercise.
References
- James Rainville, Carol Hartigan, Eugenio Martinez, Janet Limke, Cristin Jouve, Mark Finno: Exercise as a treatment for chronic low back pain. PMID: 14749199 DOI: 10.1016/s1529-9430(03)00174-8
- A Murtezani, H Hundozi, N Orovcanec, S Sllamniku, T Osmani: A comparison of high intensity aerobic exercise and passive modalities for the treatment of workers with chronic low back pain: a randomized, controlled trial: PMID: 21602759
- Rahman Shiri, David Coggon: Exercise for the Prevention of Low Back Pain: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Controlled Trials: American Journal of Epidemiology, Volume 187, Issue 5, May 2018, Pages 1093–1101
- Suh, Jee Hyun MD; Kim, Hayoung BS; Jung, Gwang Pyo MD; Ko, Jin Young MD; Ryu, Ju Seok MD, PhD: The effect of lumbar stabilization and walking exercises on chronic low back pain: June 2019 – Volume 98 – Issue 26 – p e16173 doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000016173
- Manniche C, Lundberg E, Christensen I, et al. Intensive dynamic back exercises for chronic low back pain: a clinical trial. Pain 1991;47:53–63.
- Hartigan C. Exercise-based therapy for low back pain. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/search. Accessed April 19, 2023.
- Spine conditioning program. American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/recovery/spine-conditioning-program/. Accessed April 19, 2023.
- Bydon M. Physical therapy. In: Back and Neck Health. Mayo Clinic Press; 2021.
- Dutton M. Lumbar spine. In: Dutton’s Orthopaedic Examination, Evaluation, and Intervention. 6th ed. McGraw Hill; 2022. https://accessphysiotherapy.mhmedical.com. Accessed April 24, 2023.
Bodyweight Back Workout at Home Without Equipment

Manish brings over 10 years of hands-on experience in weight lifting and fat loss to fitness coaching. He specializes in gym-based training and has a lot of knowledge about exercise, lifting technique, biomechanics, and more.
Through “Fit Life Regime,” he generously shares the insights he’s gained over a decade in the field. His goal is to equip others with the knowledge to start their own fitness journey.
