Do you want to improve your grip strength and get stronger forearms? Whether you are an athlete, weightlifter, or someone who just wants to get a bigger forearm and stronger grip, you should do forearm exercises.
Not only does it help you lift heavier weights, but it also improves your overall performance in various sports and activities.
The forearms play a pivotal role in everyday tasks like lifting, carrying, and gripping, making their strength and conditioning vital for overall performance.
In this article, we’ll share with you the following:
- Forearm Muscles
- Best Forearm Exercise
- Forearm Training Program
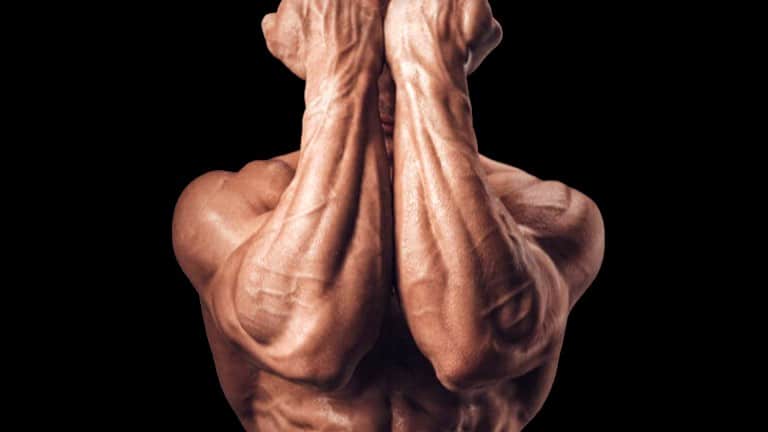

- Forearm Muscles
- Flexor Muscles
- Extensor Muscles
- Pronator and Supinator Muscles
- Brachioradialis
- The Importance Of a Stronger Forearm
- 1. Enhanced Performance
- 2. Injury Prevention
- 3. Improve Functional Abilities
- 4. Grip Strength
- 5. Improved Aesthetics
- How To Train Forearms for Stronger Grip and Wrist
- 1. Pronation
- 2. Supination
- 3. Flexion
- 4. Extension
- 25 Exercises To Make Your Forearms Bigger and Stronger
- 1. Dead Hangs
- 2. Towel Pull-Ups
- 3. Barbell Wrist Curl
- 4. Seated Dumbbell Wrist Curls
- 5. Barbell Reverse Wrist Curl
- 6. Plate Pinch
- 7. Seated Finger Curl
- 8. Dumbbell Wrist Twist
- 9. Barbell Reverse Curl
- 10. Dumbbell Reverse Preacher Curl
- 11. Behind-The-Back Barbell Finger Curls
- 12. Dumbbell Farmer’s Walk
- 13. Hammer Curl
- 14. Zottman Curl
- 15. Dumbbell Reverse Grip Concentration Curl
- 16. Hand Gripper
- 17. Fingertip Push Up
- Tips
- 18. Lateral Plank Walk
- 19. Crab Walk
- 20. Wrist Rollers
- 21. Rope Climber
- 22. Standing Dumbbell Drag Curl
- 23. Plank Row
- 24. Inverted Row
- 25. Turkish Get Up
- Advance Technique To Build Bigger and Stronger Forearms
- 1. Fat Grip Training
- 2. Eccentric Emphasis
- 3. Supersets and Drop sets
- 4. Isometric Holds
- 5. Time Under Tension
- 6. Hand Grippers and Grip Training Tools
- 7. Progressive Overload
- 8. Stretch and Mobilize
- Sets, Reps and Frequency for forearm Workout
- 1. Sets For Forearm
- 2. Repetitions (Reps) For Forearm
- 3. Frequency Of Forearm Workout
- Forearm Workout Samples plan
- 1. Beginner Forearm Workout Plan
- 2. Intermediate Forearm Workout Plan
- 3. Advanced Forearm Workout Plan
- FAQs
- Are forearm exercises necessary
- Can forearm exercises help prevent wrist and hand injuries?
- How long does it take to see results from forearm exercises?
- Is it good to do forearms every day?
- Conclusion
- Sources
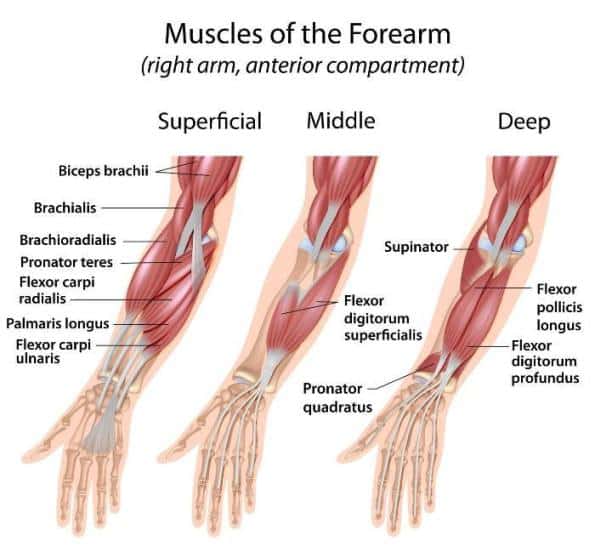
Forearm Muscles
The forearm is a complex area of the upper limb that contains numerous muscles responsible for various movements and functions.
In order to effectively target the forearm, it is essential to understand the forearm muscles.
Let’s delve into the key muscles of the forearm:
Flexor Muscles
- Flexor Digitorum Profundus: This muscle runs along the forearm and is responsible for flexing the fingers.
- Flexor Digitorum Superficialis: Positioned above the flexor digitorum profundus, this muscle flexes the fingers as well.
- Flexor Carpi Radialis: Located on the inner side of the forearm, this muscle flexes and abducts the wrist.
- Palmaris Longus: this muscle aids in wrist flexion and tenses the palmar aponeurosis.
Extensor Muscles
- Extensor Digitorum: Positioned on the back of the forearm, this muscle extends the fingers.
- Extensor Carpi Ulnaris: Located on the outer side of the forearm, this muscle extends and adducts the wrist.
- Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus and Brevis: These muscles extend and abduct the wrist.
Pronator and Supinator Muscles
- Pronator Teres: Positioned on the inner side of the forearm, this muscle pronates the forearm (rotates it to face downward).
- Pronator Quadratus: Located near the wrist, this muscle assists in pronation.
- Supinator: Situated on the outer side of the forearm, this muscle supinates the forearm (rotates it to face upward).
Brachioradialis
This muscle runs along the outer side of the forearm and aids in flexion and rotation of the forearm.
The Importance Of a Stronger Forearm
1. Enhanced Performance
Strong forearms contribute to improved performance in various activities and sports that involve gripping, lifting, and manipulating objects.
Forearm strength helps in tasks such as weightlifting, rock climbing, golf swings, racket sports, and many others.
A study published in the journal Science found a significant correlation between stronger forearms and performance in exercises such as deadlifts and bench presses.
2. Injury Prevention
Strong forearms provide stability and support to the wrist and elbow joints, which reduces the risk of strain and stress-related injuries.
A study has also shown that stronger forearms can prevent common injuries like tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis) and other overuse injuries.
3. Improve Functional Abilities
Your strong forearms improve your ability to handle everyday activities with ease and efficiency.
It is essential to have strong arms for daily functional tasks, including carrying groceries, opening jars, gripping tools, and performing manual labor.
4. Grip Strength
Grip Strength is directly related to forearm and wrist strength. A strong grasp is essential for numerous sports, work-related tasks, and activities that require a firm hold.
Developing a stronger grip can lead to improvements in other strength exercises like deadlifts, pull-ups, and rows. It can also enhance performance in exercises that require holding or manipulating weights.
5. Improved Aesthetics
Having well-developed forearms contributes to a balanced and aesthetic physique. The forearm muscles can be strengthened and toned to make the arms look bigger and more defined.
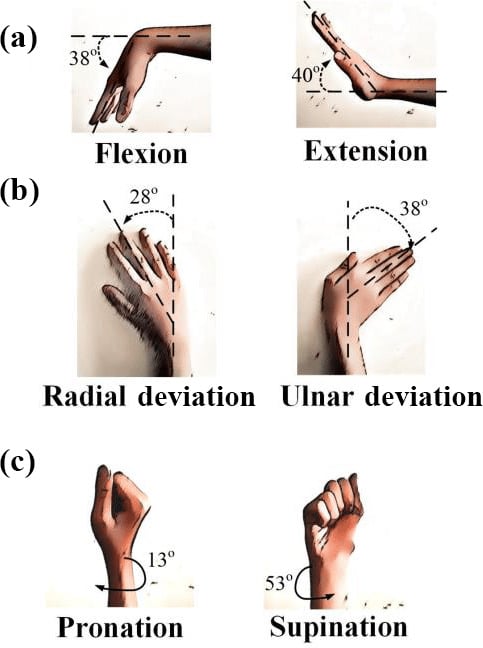
How To Train Forearms for Stronger Grip and Wrist
1. Pronation
Pronation is the rotational movement of the forearm where the palm faces downward or backward.
In pronation, the radius bone of the forearm crosses over the ulna bone, resulting in the palm facing away from the body.
This movement is commonly used when pouring liquid out of a container, turning a doorknob, or performing movements like using a screwdriver.
2. Supination
Supination is the opposite movement of pronation. It involves rotating the forearm so that the palm is facing upward or forward.
In supination, the radius and ulna bones are parallel to each other, allowing the palm to face toward the body.
Activities like holding a tray, throwing a ball with an underhand motion, or using a key in a lock require supination.
3. Flexion
Forearm flexion involves bending the elbow joint, which results in the forearm moving closer to the upper arm. During flexion, the angle between the forearm and upper arm decreases.
This movement is often seen when doing bicep curls, lifting objects towards the shoulder.
4. Extension
Forearm extension is the opposite movement of flexion. It means to move the forearm away from the upper arm by straightening or extending the elbow joint.
During extension, the angle between the forearm and upper arm increases.
Extension can be done by pushing something away from the body, doing tricep exercises.
25 Exercises To Make Your Forearms Bigger and Stronger
It’s important to choose exercises that work multiple forearm muscles at the same time to improve forearm training and grip strength.
This approach ensures efficiency, as we aim to avoid spending excessive time exclusively on forearm training.
By focusing on exercises that work the majority of the small muscles in the forearm, we can get the most out of the workout.
1. Dead Hangs
Dead hangs are a simple yet effective exercise that involves hanging from a bar or any elevated surface with an overhand grip.
The study has shown that dead hanging is an effective exercise for improving forearm and grip strength, which in turn improves climbing performance.
It also promotes scapular retraction and depression, which helps improve shoulder stability and posture.
Other variations of dead hangs to improve forearm size and strength:
- One-Arm Dead Hang
- Weighted Dead Hang
- Towel Dead Hang
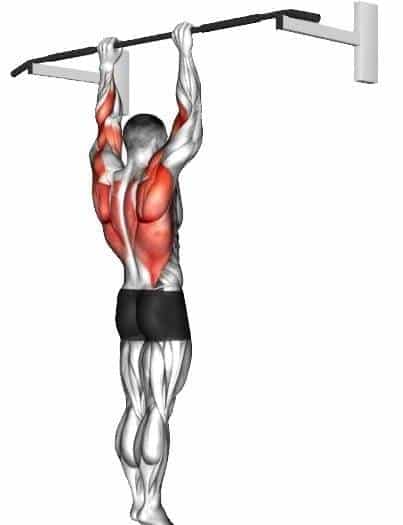
How To Do Dead Hangs
- Find a sturdy bar or similar elevated surface that can support your body weight.
- Stand beneath the bar, reach up, and grab it with an overhand grip (palms facing away from you).
- Your hands should be slightly wider than shoulder-width apart.
- Hang freely from the bar, allowing your body to fully extend. Relax your shoulders and engage your core.
- Hold the position for a designated amount of time, typically starting with 20-30 seconds and gradually increasing as your strength improves.
- Release the grip and lower yourself down gently to finish the exercise.
- Repeat for the desired number of sets.
Tips
- If you’re new to dead hangs, try shorter durations.
- Avoid swinging.
2. Towel Pull-Ups
The Towel pull-ups are a harder version of the traditional pull-up exercise that uses towels as grips.
It helps to increase muscle activation and strength in the upper body, especially in the biceps and back, as well as improve grip strength and endurance.
It places a significant demand on your grip strength, as you need to squeeze the towels tightly to maintain your hold.
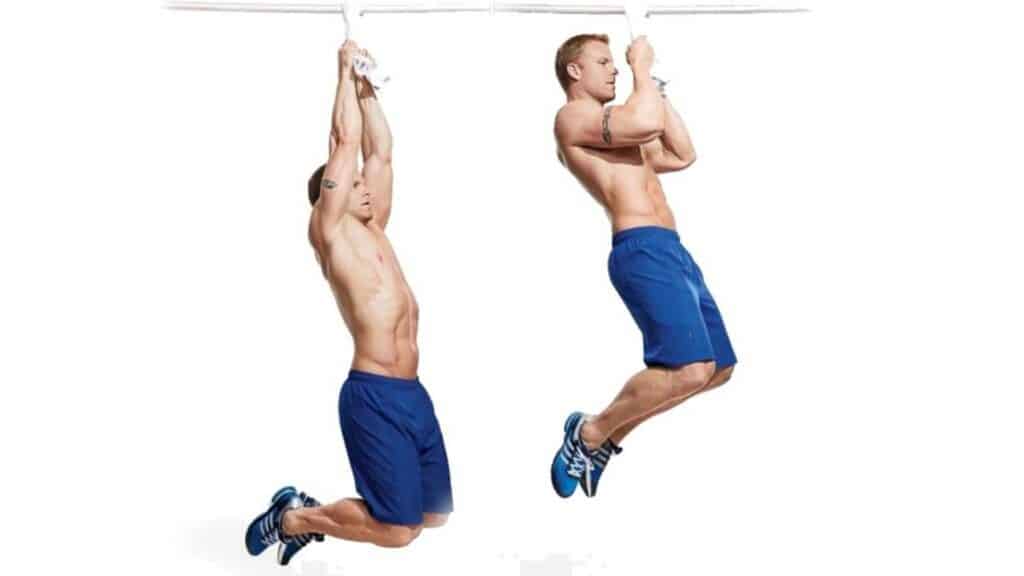

How To Do Towel Pull-Ups
- Stand beneath the bar and reach up to grab the ends of the towel.
- Hang freely from the towels, keeping your body straight and engaging your core.
- Bend your elbows and squeeze your shoulder blades together until your chin touches or clears the bar.
- Slowly lower yourself back down to the starting position with control.
- Repeat for the desired number of repetitions.
Tips
- Make sure that the length of the towels allows for a comfortable grip.
- Engage your core and avoid excessive swinging or kipping.
3. Barbell Wrist Curl
Barbell wrist curls are an exercise that targets the muscles of the forearm, specifically the wrist flexors. It is a great exercise to help improve grip strength and forearm size and definition
According to the study, a 12-week periodized forearm training program can enhance wrist and forearm strength, as well as bat-end velocity, in baseball players.
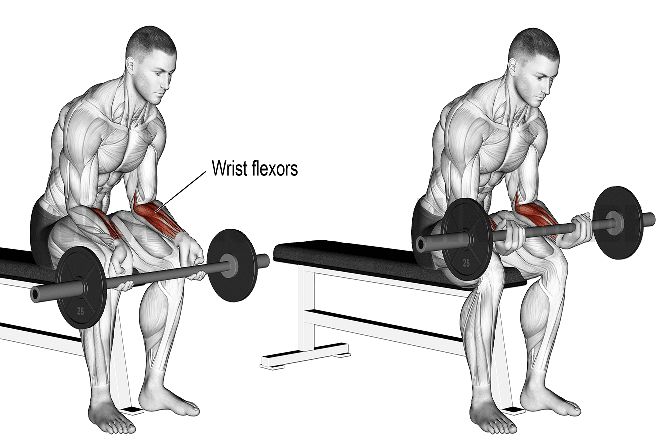
How To Do Barbell Wrist Curl
- Grasp the barbell with an underhand grip.
- Rest your forearms on the bench with your palms facing up and the backs of your wrists resting on the bench/Quads.
- Slowly lift the barbell by flexing your wrists, keeping your forearms flat on the bench.
- Pause at the top of the movement, then slowly lower the barbell back down to the starting position.
- Repeat for the desired number of repetitions.
Tips
- Use a weight that you can comfortably control throughout the entire range of motion.
4. Seated Dumbbell Wrist Curls
Seated dumbbell wrist curls are isolation exercises that primarily target the muscles responsible for wrist flexion, specifically the wrist flexor group.
It is a simple but effective exercise that helps to strengthen the muscles in the forearms and wrists.
The exercise is typically performed using a barbell or a pair of dumbbells and it can be done seated or standing.
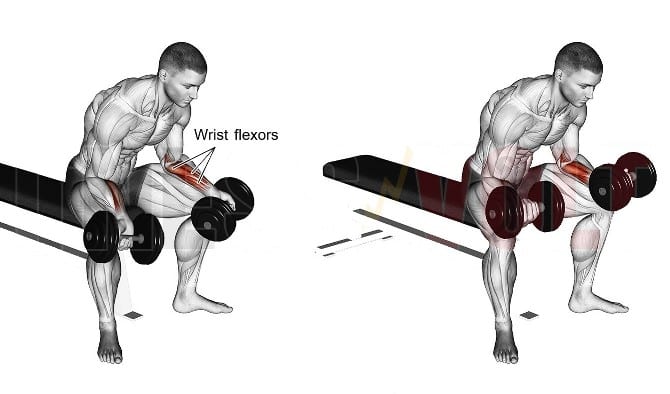
How To Do Palms-Up Wrist Curl
- Sit on a flat bench with your legs bent and your feet flat on the floor.
- Place your forearms on your thighs, with your wrists hanging off the edge.
- Hold a barbell or a pair of dumbbells with your palms facing up.
- Slowly bend your wrists to lower the weight towards your fingers, keeping your upper arms stationary.
- Hold for a moment at the bottom of the movement, then slowly extend your wrists to raise the weight back to the starting position.
- Repeat for the desired number of reps and sets.
5. Barbell Reverse Wrist Curl
Barbell Reverse wrist curls are similar to regular wrist curls, but with a reversed hand position. It primarily targets the forearm muscles, particularly the brachioradialis and wrist extensors.
Strong extensor muscles contribute to better grip stability and control. This can be beneficial in activities that require a firm grip, such as weightlifting, racket sports, and manual labor.
Other ways to improve forearm size and strength with a reverse wrist curl are:
- Reverse Dumbbell Wrist Curl
- Cable Reverse Wrist Curl
- Single Arm Reverse Wrist Curl
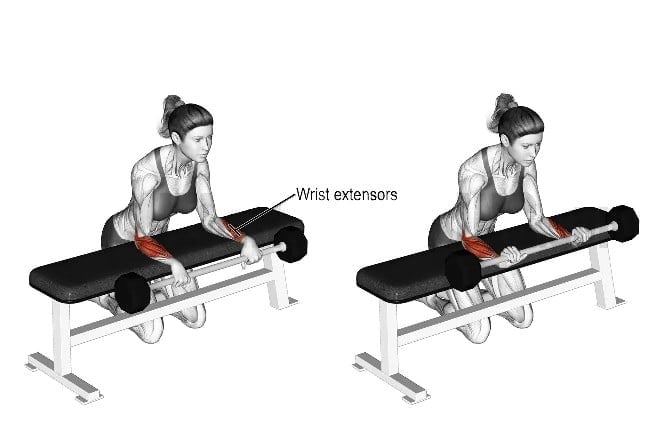
How To Do Reverse Wrist Curl
- Grab a barbell with an overhand grip.
- Lift the barbell up by flexing your wrists and raising your hands towards your forearms.
- Slowly lower the barbell back down to the starting position by extending your wrists.
- Repeat for the desired number of reps
Tips
- Avoid using momentum to lift the weight and focus on contracting your forearm muscles.
6. Plate Pinch
The Plate Pinch exercise is a great way to strengthen the muscles in the fingers, hands, and forearms.
It is typically performed using a weight plate, and it works the grip, the strength and dexterity of the fingers and hands.
Plate pinch exercises improve grip endurance by making you hold on to weight plates for a long time. This makes you stronger and can be useful for sports like climbing rocks, fighting, and carrying or holding things for a long time.
How To Do Plate Pinch
- Start by selecting a weight plate that is comfortable to hold but still challenging.
- Hold the weight plate with your thumb and fingers, with your hands positioned on the edges of the plate.
- Pinch the plate firmly between your fingers and thumb, making sure to keep your wrists straight.
- Hold the plate for the desired amount of time, trying to maintain a steady grip and hold throughout the duration of the exercise.
- Release the weight plate, rest for a moment, and repeat the exercise for the desired number of sets and reps.
7. Seated Finger Curl
The seated finger curl is a finger and forearm exercise that specifically targets the muscles responsible for finger flexion. It is particularly effective for strengthening the fingers and grip strength.
A solid grip and strong fingers are beneficial for activities that require grasping, holding, or manipulating objects, such as weightlifting, rock climbing, and everyday tasks.
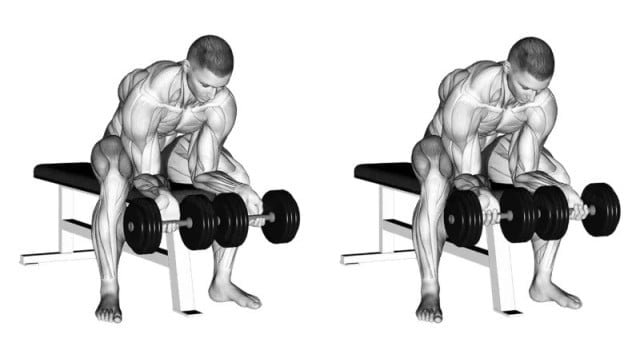
How To Do Dumbbell Finger Rolls
- Sit on a bench or chair with your back straight and feet flat on the floor.
- Hold a dumbbell in each hand, palms facing up.
- Start with the dumbbells hanging at arm’s length in front of your thighs.
- Lower the dumbbells as far as possible by extending your fingers, allowing them to roll down your hands.
- Catch the dumbbells with the final joint in your fingers.
- Curl the dumbbells up as high as possible by closing your hands, flexing your fingers, and squeezing the dumbbells.
- Exhale as you curl the dumbbells up and hold the contraction at the top for a moment.
- Slowly lower the dumbbells back to the starting position, extending your fingers and allowing the dumbbells to roll down your hands.
- Repeat for the desired number of repetitions.
8. Dumbbell Wrist Twist
The dumbbell wrist twist, also known as pronation and supination, is an exercise that focuses on strengthening the muscles responsible for rotating the forearm, specifically the pronators and supinators forearm muscles.
It involves holding a dumbbell and rotating the wrist to perform pronation (inward rotation) and supination (outward rotation) movements.
This exercise mimics the rotational movements required in many daily activities and sports, such as turning a doorknob, swinging a golf club, or throwing a ball.
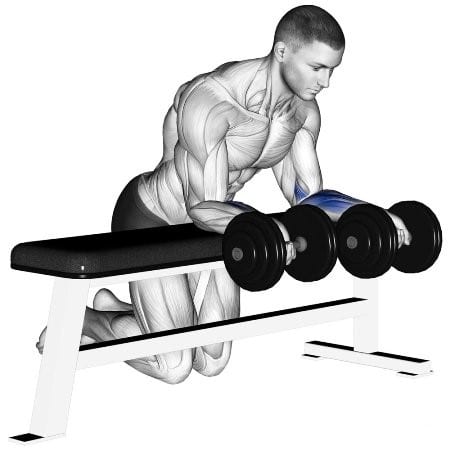

How To Do Dumbbell Wrist Twist
- Stand or sit with proper posture and hold a dumbbell with an underhand grip (palms facing up) in one hand.
- Rest your forearm on a bench or thigh, keeping your wrist just beyond the edge and allowing it to move freely.
- Start with the dumbbell hanging down, parallel to the floor, and your palm facing inward (pronation).
- Slowly rotate your wrist outward, moving the dumbbell upward until your palm is facing upward (supination).
- Pause briefly at the top of the movement, then rotate your wrist back inward to return to the starting position.
- Repeat for the desired number of repetitions, and then switch to the other hand.
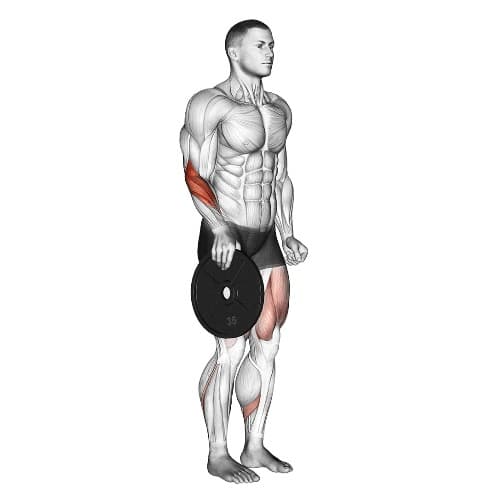
9. Barbell Reverse Curl
The barbell reverse curl is a non-negotiable component of a barbell arm workout that primarily targets the muscles of the forearm, particularly the brachioradialis.
The pronated grip increases the engagement of the brachioradialis muscles. It requires stabilization of the wrists throughout the exercise.
This helps make your wrists stronger and more flexible. This is helpful for doing things like turning, turning, and controlling things with your hands and wrists.
Other variations of reverse curl to improve forearm mass and strength:
- Dumbbell Reverse Curl
- Cable Reverse Curl
- One Arm Reverse Curl

How To Do Barbell Reverse Curl
- Grab the bar with a shoulder width grip with your hands on top of the bar (pronated grip)
- Curl the bar up to shoulder level by bending your elbows.
- Lower the bar back down to the arms’ extended position.
- Repeat for desired reps.
Tips
- Your body should remain fixed. Only your biceps should be used to move the weight.
- The motion should occur at the elbow.
- Ensure that your elbows are kept close to your sides with your knees slightly bent, and your hands gripped tightly to the bar.
10. Dumbbell Reverse Preacher Curl
The reverse preacher curl is a variation of the standard preacher curl targeting your brachialis muscle, which lies deeper than your biceps brachii in the upper arm.
The brachialis and brachioradialis muscle help the flexion of the elbows, while the wrist flexors act as stabilizer muscles, undergoing contraction.

How To Do Dumbbell Reverse Preacher Curl
- Adjust the preacher bench seat so that your arms are level with the top of the bench.
- Grab a dumbbell in each hand with a pronated (palms down) grip and rest your arm against the bench with your arm extended fully down.
- Slowly curl the dumbbells up towards your head, keeping your arms on the bench at all times, until you reach the top position.
- Hold for a count, squeeze and isolate your biceps.
- Repeat the desired number of repetitions.
Tips
- Make sure that you perform the movement slowly with controlled repetition timing.
- Do not lock out your elbows at the bottom of the reverse curl, as this can cause a torn bicep and takes tension off the muscle.
- Try to use a lighter to moderate weight.
11. Behind-The-Back Barbell Finger Curls
Behind-the-back barbell finger curls are a variation of finger curls that primarily focus on strengthening the muscles of the fingers and forearms.
Behind your back curl, increases the range of motion and puts more emphasis on finger flexion.
Try other variations of the behind-the-back finger curls to build up strength and mass in your forearm:
- Dumbbell Behind-The-Back Finger Curls
- Single arm Behind-The-Back Finger Curls
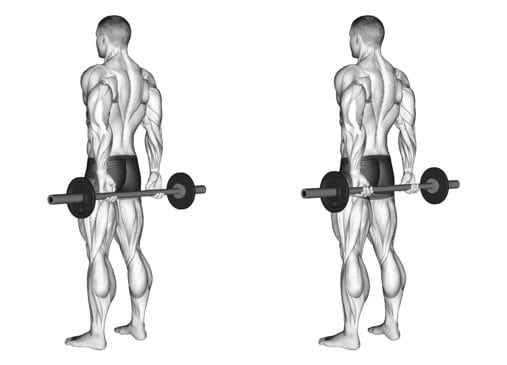
How To Do It
- Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart and hold a barbell behind your back, with your palms facing backward.
- Let your arms naturally hang down, with the barbell behind your hips.
- Keeping your arms still, curl your fingers and squeeze, flexing your fingers as much as you can.
- Hold the contracted position for a moment, then slowly release and extend your fingers to return to the starting position.
- Repeat for the desired number of repetitions.
12. Dumbbell Farmer’s Walk
The Farmer’s walk is a functional exercise that can be used to build overall grip and forearm strength. The exercise involves holding a pair of heavy dumbbells at your sides and walking with them for a set distance or time.
It is relatively simple to perform, but can be quite challenging as the weight used for this exercise is usually quite heavy.
This exercise can be quite challenging, it is recommended to start with a moderate weight, and increase it gradually as you build up your strength.
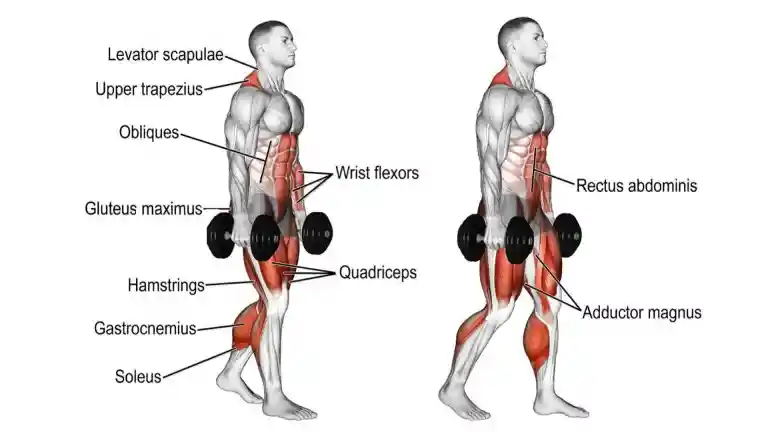
How To Do Farmer’s Walk
- Start by selecting a pair of heavy dumbbells, which are challenging but still manageable to hold.
- Stand with your feet hip-width apart and your knees slightly bent.
- Take a dumbbell in each hand and let them hang at your sides.
- Keep your back straight and your core engaged throughout the exercise.
- Begin walking forward, keeping a steady pace and maintaining good form.
- Walk for the desired distance or time, then release the weight and rest for a moment before repeating.
13. Hammer Curl
The Hammer Curl is a classic weightlifting exercise that targets the biceps and brachialis.
When it comes to building muscular hypertrophy and strength, the hammer curl exercise is one of the most popular brachialis exercises among bodybuilders and regular weightlifters.

How To Do Hammer Curl
- Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart and a slight bend in your knees.
- Hold a pair of dumbbells in your hands with your palms facing towards your body.
- Keeping your elbows close to your body, slowly curl the dumbbell up to your shoulders.
- At the top of the lift, pause for a second and squeeze your brachialis, then lower the weights under control.
Tips
- Raise and lower the dumbbell slowly. Keep in control by using your own strength, not using momentum or gravity.
- Neither lean back as you lift the weight nor lean forward as you lower it.
14. Zottman Curl
The dumbbell zottman curl is one of the best variations of the standard bicep curl. It utilizes different hand positioning at different portions of the lift.
The first portion, the regular curl, focuses on bicep strength. You can perform Zottman curls with both arms at the same time, or alternate the arm you lift with.

How To Do Zottman Curl
- Hold a pair of dumbbells to your sides.
- Keep your palms facing up as you curl the weights up to your shoulders. Pause at the top of the movement.
- Slowly rotate your grip, so your palms are facing downwards.
- Lower the dumbbells slowly back to the starting position using an overhand grip.
- When the dumbbells are close to your thighs, again turn your hands while returning to the starting position.
Tips
- Perform this exercise in a slow, controlled manner for best results.
- Don’t go heavy. Choose a lighter weight and focus on perfecting your form.
15. Dumbbell Reverse Grip Concentration Curl
The Reverse Grip Dumbbell Concentration Curl is a great basic move. When done correctly, it can effectively target your arms, forearms, and upper body.
It is an isolation exercise that targets the biceps brachii and brachialis muscles.

How To Do Reverse Grip Concentration Curl
- Sit on a bench with your legs apart, grab a dumbbell in one hand (say left hand).
- With your left arm almost fully extended, rest your elbow against the inside of your left thigh.
- Pronate your wrist so that your palm faces backward.
- Exhale as you curl the dumbbell up towards your shoulder. Hold and squeeze your biceps for a count of two.
- Inhale as you slowly lower the dumbbell to the starting position.
- Repeat with your right arm.
Tips
- Don’t lockout at the bottom of the exercise.
- Keep your back straight and your upper arm still.
16. Hand Gripper
Hand gripper exercises are specifically designed to target forearm and improve grip strength. They engage the muscles of the hands, fingers, and forearms. It enhances the strength of grip and hand dexterity.
Hand grippers are compact and portable, making them convenient for use anywhere, whether at home, the office, or while traveling.
They provide a quick and effective way to work on grip strength without requiring a full gym setup.
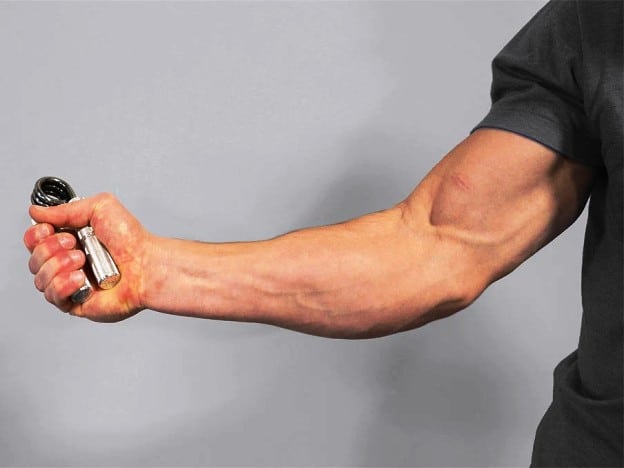
How To Do Grip Squeezes with Hand Grippers
- Choose a hand gripper with an appropriate resistance level.
- Beginners may start with a lower resistance gripper.
- Hold the hand gripper in one hand, ensuring a firm grip on the handles.
- Position your hand so that your fingers are wrapped around the handles and your thumb is placed on the opposite side for support.
- Squeeze the handles together using your fingers and thumb, applying steady and controlled force.
- Hold the gripper in the squeezed position for a few seconds, then slowly release it back to the starting position.
- Repeat for the desired number of reps.
Tips
- Avoid using excessive wrist movement or relying solely on finger strength.
- Start with a gripper resistance that will challenge you but also allow you to perform the exercises with proper form.
17. Fingertip Push Up
Fingertip push ups places greater emphasis on the fingers, hands, and forearms while engaging the chest, shoulders, tricep. It also challenges your core muscles to keep your body balanced.
It’s also an efficient exercise to increase your grip for basketball, bodybuilding, or rock climbing.
It also keeps your wrists straight, making it an excellent way to eliminate wrist pain from the 90-degree bend when your palms are flat on the floor.
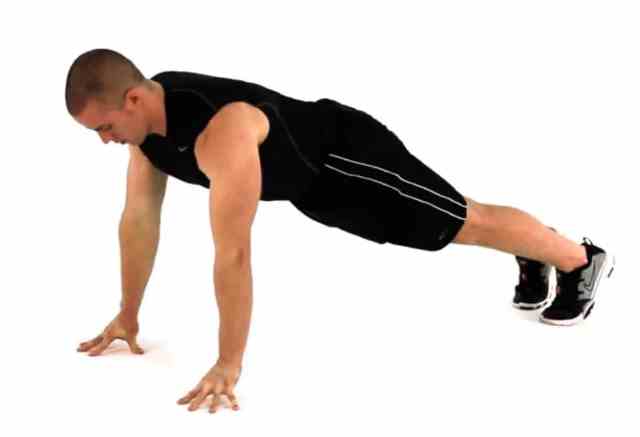

How To Do Fingertip Push-Ups
- Take a standard push-up position, your fingertips are in contact with the ground.
- Position your fingers so that your fingertips are the only parts of your hand in contact with the ground.
- Engage your core muscles to maintain a straight line from your head to your heels.
- Lower your body by bending your elbows, keeping them close to your sides, until your chest nearly touches the ground.
- Push yourself back up by extending your arms, returning to the starting position.
- Repeat for the desired number of repetitions.
Tips
- If fingertip push-ups are hard at first, you can start by doing them with your knees on the ground.
- Engage your core muscles and avoid moving your hips too much or making them sag.
Know More: 20 Different Types Of Push Ups For Mass And Strength
18. Lateral Plank Walk
The Lateral Plank Walk is a full-body exercise that mainly targets your core, shoulders and arms. Take a walk on the wild side as well, as wild as a plank can get.
This move intensely engages your core like a classic plank, but the side-to-side motion works your arms and delts, too. Plus, it’ll challenge your balance and stability.
The faster you “walk,” the more challenging this will be cardiovascular. Slow down if you need to dial down the intensity a bit.
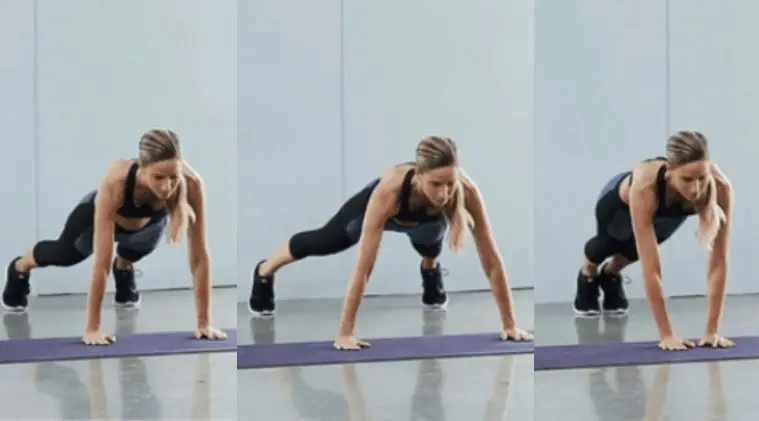

How To Do Lateral Plank Walk
- Start in a high plank position.
- Your body should form a straight line from your shoulders to your ankles.
- Take a step to the right starting with your right hand and right foot and following with your left hand and foot, maintaining a plank position as you move.
- Do a set number of reps in one direction, and then repeat the same number of reps moving in the opposite direction.
Tips
- Avoid sagging or raising your hips.
- Avoid rushing the movement.
Know More: Plank Exercise: Benefits, Variations, Muscles Worked, Tips
19. Crab Walk
The Crab walk is an excellent bodyweight exercise that particularly works the arms, shoulders, legs, and core.
It is excellent for toning, effectively targeting all your muscle groups and working them hard to build strength.
Moves like the crab walk are great total-body exercises that don’t require any additional equipment, making them ideal moves to perform when you don’t have a lot of time or fitness gear on hand.
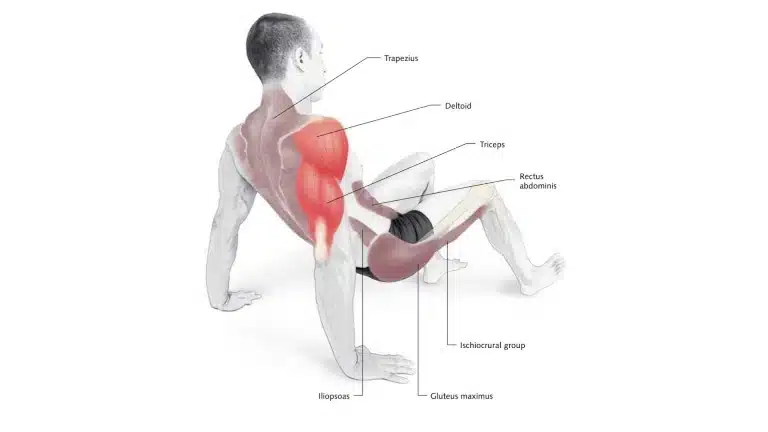
How To Do Crab Walk
- Position your hands and feet so that they are flat on the ground, and you are the face up.
- Lift your butt up off the ground by tightening your gluteal muscles.
- Begin “walking” by first moving your hands and then your feet.
- Avoid excessive shoulder strain by moving your hands no more than 6 to 8 inches (15 to 20 cm) at a time.
Tips
- As a caution, do not let your feet get moving too fast for your upper body so as not to injure your shoulders.
- Control your movements
20. Wrist Rollers
A wrist roller is a simple tool consisting of a bar or rod with a rope or cord attached to it. You attach weights to the other end of the rope, and by rolling the device, you engage the muscles in your wrists and forearms.
Rolling motion strengthens the supporting muscles and tendons in the wrist, improving joint stability and range of motion.
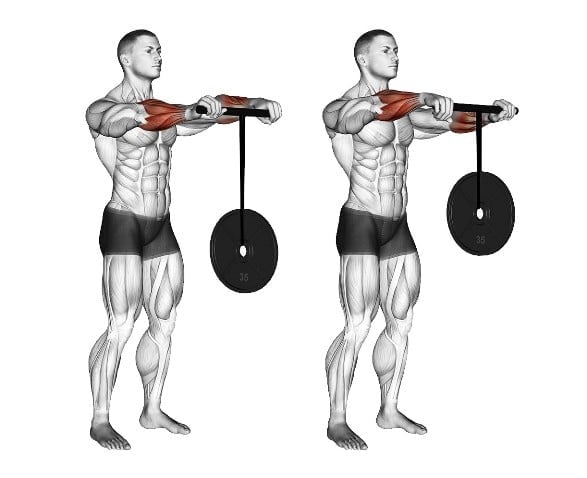
How To Do Wrist Rollers
- Start by attaching the desired amount of weight to the end of the rope or cord.
- Hold the bar or rod with both hands, palms facing down.
- Keep your elbows slightly bent as you extend your arms in front of you.
- Start rolling the wrist roller by moving your hands forward and letting the weight go up toward the bar.
- Keep rolling until the weight reaches the bar, then turn around and roll it back up to where you started.
- Repeat the movement for the desired number of repetitions
Tips
- Keep your wrists in a neutral position.
- Avoid rapid or jerky motions.
- It is important to emphasize the eccentric (lowering) phase of movement.
21. Rope Climber
Rope climbs require you to use your arms and upper body strength to climb up a vertical rope, while using your legs for support and balance.
It is a full-body exercise that primarily targets the muscles in the upper body, including the forearms, back, and shoulders.
Since rope climbs heavily rely on gripping the rope, they provide an effective way to improve grip strength and endurance.
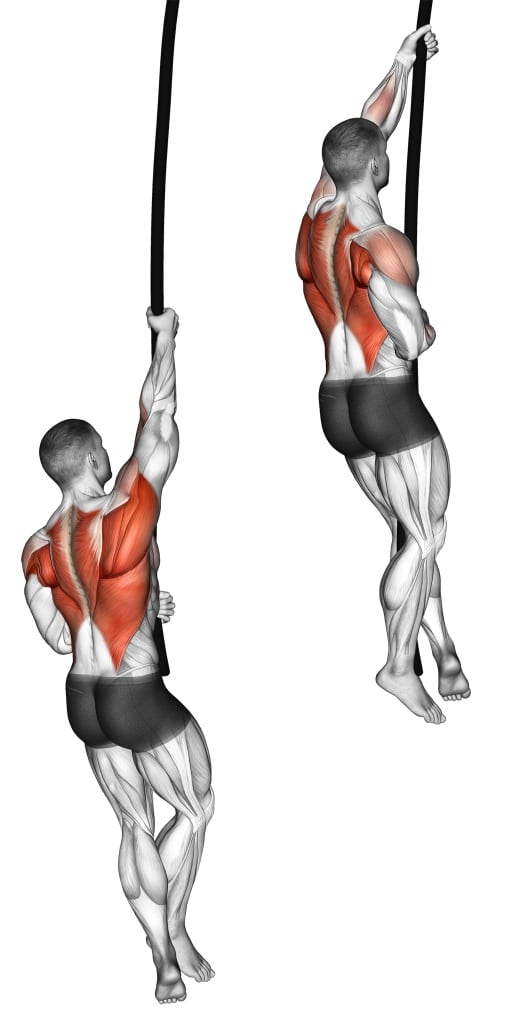
How To Do Rope Climber
- First, make sure you have a strong rope that can hold your weight.
- Reach up and grab the rope with both hands.
- You can begin the climb by using your arms to pull yourself upward while simultaneously pushing with your legs.
- Use a hand-over-hand technique, alternating your hands and legs to move up the rope.
- Maintain a strong grip on the rope and continue climbing until you reach your desired height or the top.
- To descend, either reverse the climbing motion or use a controlled descent technique, such as wrapping your legs around the rope and sliding down.
Tips
- Start with shorter climbs.
- To prevent rope burn or discomfort, wear long socks.
22. Standing Dumbbell Drag Curl
The dumbbell drag curl is a variation of the dumbbell curl and is used to build bicep and forearm muscles
The dumbbell drag curl is a unique bicep curl variation in which you don’t completely bring the weight in front of your body, which makes it more difficult to swing and use momentum to get the weight up.
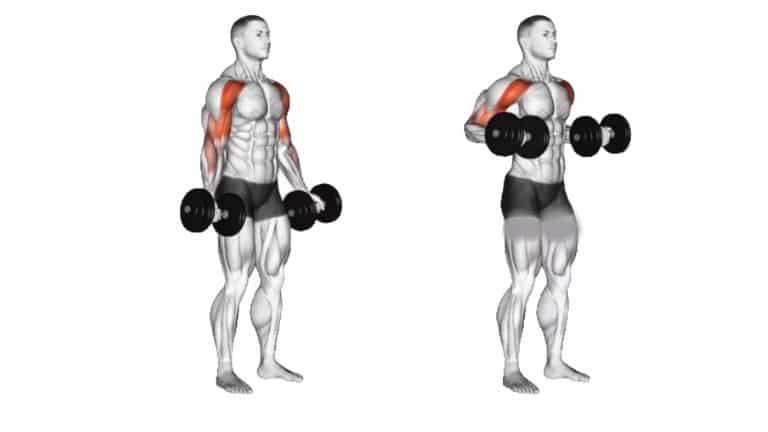
How To Do Standing Dumbbell Drag Curl
- Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart, your knees slightly bent and your abs are drawn in.
- Grab the dumbbell with a double underhand (supinated) grip with your hands slightly wider than shoulder-width apart.
- Bring your elbows and shoulders back slightly as you curl the Dumbbells upwards.
- It should feel like you are “dragging” the dumbbell up to your body.
- Squeeze your biceps hard at the top and slowly return to the starting position.
23. Plank Row
Plank Row aka Renegade rows are a challenging exercise that targets multiple muscle groups simultaneously, including the core, back, shoulders, and arms.
The rowing motion in plank rows primarily targets the muscles in the upper back, including the latissimus dorsi, rhomboids, and rear deltoids.
Additionally, it engages the muscles of the arms, such as the forearm, biceps, and triceps.
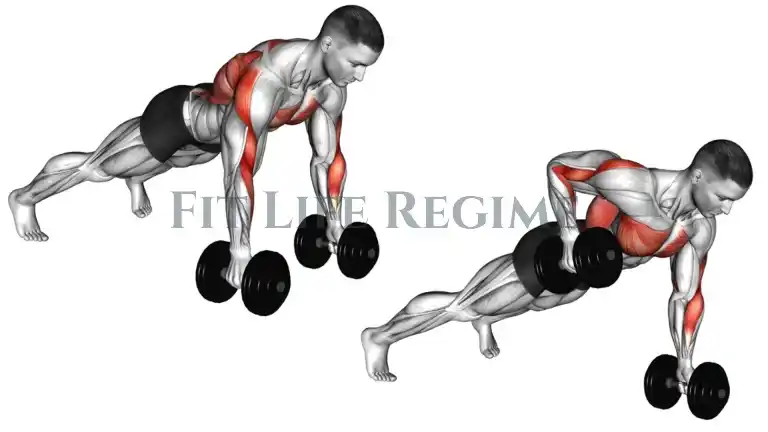

How To Do Plank Row
- Place two dumbbells on the floor about shoulder-width apart.
- Start in the top position of a push-up position with your hands on the weights.
- Pull right elbow back, raising dumbbell toward chest, keeping right elbow close to the torso, abs tight, and hips in one line.
- Hold for one second at the top and return the weight slowly to the starting position to repeat on the other side.
- Complete the desired number of repetitions.
24. Inverted Row
The inverted row (bodyweight rows) creates a horizontal body position, making it easier to perform. It works the back and shoulder and forearm muscles from a different angle and improves upper body strength.
In the gym, most people utilize the Smith machine for this exercise.
You can also do the inverted row at home by lying under a chair and pulling yourself up.

How To Do Inverted Row
- Adjust the height of the chair and bar so that it’s a little higher than arm’s length from the floor.
- Lie under the bar with your legs and body straight.
- Grasp the bar with an overhand grip that’s a little wider than shoulder width.
- Keeping your legs and body straight, exhale as you pull your chest up to the bar.
- Hold for a count of two and squeeze your back muscles.
- Breathe in as you lower your body until your arms and shoulders are fully extended. Repeat.
Tips
- Do not allow your butt to sag.
- Keep your elbows tucked in.
- Lower your body until the arms are fully extended, and then raise your body until the chest touches the bar.
25. Turkish Get Up
The Turkish Get Up is a complex movement that engages multiple muscle groups and challenges stability, strength, and coordination.
It originated from an ancient Turkish training method and has become a popular exercise in strength and conditioning programs.
It targets almost every major muscle group, including the core, forearm, shoulders, glutes, hips, and legs.

How To Do It
- Lie on your back on the floor and hold a dumbbell in one hand with your arm fully extended above your chest.
- Bend the knee of the same side to a 90-degree angle.
- Keep your opposite leg straight, and place it 5-10 degrees away from the midline of your body.
- Start by lifting the dumbbell to the sky, and crunching onto your opposite elbow.
- Keep the elbow of the arm holding the dumbbell locked out.
- Hike your hips in the air and sweep the straight leg underneath the body, stepping back and settling onto your knee.
- Shift the weight away from your hand and onto your knee and front foot as you bring your torso upright.
- Push to a standing position, keeping the dumbbell lifted the entire time. Lower slowly back to the ground.
Tips
- Make sure you keep your elbow locked out throughout the exercise.
- Keep your eyes focused on the dumbbell throughout the entire movement.
Advance Technique To Build Bigger and Stronger Forearms
In order to build bigger and stronger forearms, it is important to incorporate advanced techniques that challenge the muscles and promote progressive overload.
Here are some advanced techniques you can incorporate into your forearm training:
1. Fat Grip Training
Fat grip training involves the use of specialized attachments or grips that increase the diameter of the handles on dumbbells, barbells, or other equipment.
The study shows that Fat grip training may increase Electromyography (EMG) muscle activity in the forearm muscles.
Thicker handles encourage greater engagement of the forearm muscles and intensify the workout.
This technique makes the forearms work harder to keep grip strength and stability, which leads to more muscle activation and growth.
2. Eccentric Emphasis
To grow your forearm muscles even more, focus on the eccentric part of the exercise.
For example, during wrist curls or reverse wrist curls, you can emphasize the lowering phase by slowing down the movement and resisting the weight.
The eccentric phase places greater stress on the muscles, which leads to increased microtrauma and subsequent muscle hypertrophy.
3. Supersets and Drop sets
Add supersets and drop sets to your forearm workouts to increase intensity and maximize muscle recruitment.
- Supersets involve performing two exercises back-to-back without rest. For example, combine wrist curls with reverse wrist curls.
- Drop sets are exercises where you do a set of exercises until you fail, then you reduce the weight and do another set.
This technique pushes the muscles to their limits and promotes muscle growth.
4. Isometric Holds
Isometric holds involve holding a position without joint movement, which activates the muscles in a static contraction.
To perform an isometric hold, hold a heavy dumbbell or barbell for a specified duration. Or, you could try doing a stationary hanging.
Isometric holds target the forearms’ stabilizing muscles, improving grip strength and overall forearm stability.
5. Time Under Tension
Focus on increasing the time under tension during forearm exercises. Slow down the tempo of the movement, emphasizing both the concentric (lifting) and eccentric (lowering) phases.
This prolonged tension on the muscles increases muscle fiber recruitment and can promote greater forearm strength and size.
6. Hand Grippers and Grip Training Tools
Hand grippers and grip training tools are devices specifically designed to target grip strength and forearm muscles.
These tools make your hand work harder by squeezing or holding it, which challenges the muscles involved in gripping and squeezing motions.
7. Progressive Overload
Enhance your forearm strength by progressively increasing the intensity of the exercises. Increase the weight, repetitions, or intensity of your workouts over time.
This progressive overload stimulates muscle growth and strength gains in the forearms.
8. Stretch and Mobilize
Keep your arms flexible and mobile with regular stretching and movement exercises to avoid muscle imbalances.
Exercise such as wrist extensions, wrist flexor stretches, and forearm pronation/supination stretches can help improve range of motion and reduce the risk of injury.
Sets, Reps and Frequency for forearm Workout
Forearm exercises should be performed at a frequency that is appropriate for each individuals’ fitness level, goals, and recovery ability.
Nevertheless, there are some general guidelines to help you get started.
1. Sets For Forearm
- Beginners: Start with 2-3 sets per exercise.
- Intermediate: Aim for 3-4 sets per exercise.
- Advanced: Perform 4-5 sets per exercise.
2. Repetitions (Reps) For Forearm
- Strength and Power: Focus on lower reps (around 6-8) with heavier weights to challenge the muscles and promote strength gains.
- Hypertrophy (Muscle Growth): Aim for moderate reps (around 8-12) with weights that fatigue the muscles within the desired rep range.
- Endurance: Perform higher reps (around 12-15 or more) with lighter weights to build muscular endurance.
3. Frequency Of Forearm Workout
- Beginners: Start with 1-2 forearm workouts per week, allowing ample recovery time between sessions.
- Intermediate: Aim for 2-3 forearm workouts per week, with at least two days of rest in between.
- Advanced: Perform 3-4 forearm workouts per week, incorporating variety in exercises and intensity levels.
Forearm Workout Samples plan
1. Beginner Forearm Workout Plan
| Exercise | Reps | Sets |
|---|---|---|
| Barbell Wrist Curls | 10-12 | 3 |
| Reverse Dumbbell Wrist Curls | 10-12 | 3 |
| Farmer’s Walk (with Dumbbells) | 30 seconds | 3 |
2. Intermediate Forearm Workout Plan
| Exercise | Reps | Sets |
|---|---|---|
| Dumbbell Wrist Curls | 8-10 | 4 |
| Reverse Barbell Wrist Curls | 8-10 | 4 |
| Behind-the-Back Wrist Curls | 10-12 | 3 |
3. Advanced Forearm Workout Plan
| Exercise | Reps | Sets |
|---|---|---|
| Dumbbell Wrist Curls | 6-8 | 5 |
| Reverse Dumbbell Wrist Curls | 6-8 | 5 |
| Behind-the-Back Wrist Curls | 8-10 | 4 |
| Dumbbell Wrist Twist | 10-12 | 3 |
FAQs
Are forearm exercises necessary
Yes, forearm exercises are necessary if you want to develop forearm strength, improve grip strength. The forearms play a crucial role in various daily activities and sports that involve gripping, lifting, and carrying objects.
Can forearm exercises help prevent wrist and hand injuries?
Yes, forearm exercises can help prevent wrist and hand injuries by strengthening the muscles, tendons, and ligaments around these areas.
Better strength and stability can provide better support and protection, which can reduce the risk of common overuse injuries, like wrist sprains or tendonitis.
How long does it take to see results from forearm exercises?
The time it takes to see results from forearm exercises can vary depending on many things like your genes, how often you do them, and how hard you work. With regular training, you can usually see improvements in forearm strength and grip within a few weeks to a couple of months.
Is it good to do forearms every day?
No, it is not recommended to perform forearm exercises every day. Like any other muscle group, the forearms need enough rest and recovery time to heal and grow stronger. Overtraining the forearms without enough rest can lead to injuries and slow progress.
It is generally recommended to allow at least 48 hours of rest between forearm workouts to ensure optimal recovery and muscle growth.
Conclusion
Dumbbell forearm exercises are an excellent way to improve your grip strength and wrist stability. Dumbbells provide a versatile and effective way to train your forearms, providing movement variability and the ability to perform unilateral exercises.
With just a dumbbell in each hand, you can achieve impressive results. For improved performance, it is important to target the wrist flexor, extensor, pronator, and supinator muscles.
To ensure continued progress, it’s important to continuously challenge yourself. As you get better at the exercises, try increasing the weights, adding new exercises, or changing the intensity or volume of your workouts.
Sources
- Mathiowetz, V., et al. (2004). Grip and Pinch Strength: Norms for 6- to 19-Year-Olds. The American Journal of Occupational Therapy, 58(2), 97-104.
- Stasinopoulos, D., & Johnson, M. I. (2007). Cyriax Physiotherapy for Tennis Elbow/lateral Epicondylitis. British Journal of Sports Medicine, 41(11), 639-642.
- Mark D Peterson. et al Low Normalized Grip Strength is a Biomarker for Cardiometabolic Disease and Physical Disabilities Among U.S. and Chinese Adults. Multicenter Study J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci2017 Oct 12;72(11):1525-1531. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glx031.

Manish brings over 10 years of hands-on experience in weight lifting and fat loss to fitness coaching. He specializes in gym-based training and has a lot of knowledge about exercise, lifting technique, biomechanics, and more.
Through “Fit Life Regime,” he generously shares the insights he’s gained over a decade in the field. His goal is to equip others with the knowledge to start their own fitness journey.
