Are you looking for the best exercises to build bigger and stronger back muscles? We have everything you need. Please continue reading to gain insight into the most effective exercises for enhancing your back size and strength.
When it comes to back muscles, the focus is usually all about the lats. However, if you want a well-rounded, strong, and good-looking back, you can’t forget to train traps, rear delts, rhomboids and erector spinae.
If you neglect and fail to strengthen them alongside the other muscles in your back, it can lead to poor posture, decreased performance, and even injury down the line.
Strengthening your complete back is absolutely necessary for achieving the best possible physique and fitness level.
In this article, you will learn
- How to train your back effectively for growth
- Back muscle anatomy
- Best back exercises for mass and strength
- Back Workout Training Techniques
- Sets and Reps
- Back workout plan for beginners, intermediate and advance.

- How To Train Back To Build Muscles Mass and Strength
- Know About Back Muscle
- Superficial Muscles
- Intermediate Muscles
- Intrinsic Muscles
- 12 Best Back Exercises To Build Bigger Back
- 1. Lat Pulldown
- How To Do It
- Tips
- 2. Barbell Shrug
- How To Do It
- Tips
- 3. Pull-Up
- How To Do It
- Tips
- 4. Barbell Upright Row
- How To Do It
- Tips
- 5. Deadlift
- How To Do It
- Tips
- 6. Bent Over Barbell Rows
- How To Do It
- Tips
- 7. Lumbar Hyperextension
- How To Do It
- Tips
- 8. Seated Cable Rows
- How To Do It
- Tips
- 9. One Arm Dumbbell Rows
- How To Do It
- Tips
- 10. T Bar Rows
- How To Do It
- Tips
- 11. Dumbbell Pullover
- How To Do It
- Tips
- 12. Straight Arm Lat Pulldown
- How To Do It
- Tips
- Bonus: Chin Up
- How To Do It
- Tips
- Complete Back Workout To Build Mass
- Sets and Reps For Back Workout
- Sets
- Reps
- Back Training Plan As Per Your Goal
- Back Exercises Workout Samples
- Beginner Back Workout Plan
- Intermediate Back Workout
- Advanced Back Workout
- FAQ About Back Training
- What is the king of all back exercises?
- Can I do back exercises everyday?
- How To Train Upper, Middle and Lower Back
- Conclusion
- References
- Best Barbell Back Exercises For Mass And Stronger
How To Train Back To Build Muscles Mass and Strength
The training of the muscles of the back is a complicated endeavor, there are many exercises that are designed to address this different region of the back.
Most of the back exercises are pulling exercises, meaning they involve a weight being pulled towards you in either a horizontal (think barbell and dumbbell rows) or vertical (think pull-ups and lat pull-downs) movement plane.
Some back exercises are back extensors, such as when you are doing a deadlift or a back extension. The primary muscles for this are the multitudes and erector spinae.
From the lat pull-down and back extension machines to pull-up bars and free weights, the options seem endless. Of course, there is good reason for this, as the muscles of the back vary tremendously in terms of their functions and angles of contraction.
Some people prefer to perform back exercises and workouts for strength, while others are more interested in back workouts for building muscle.
Again, the different goals for training will mostly affect how many reps, sets, and weights are done for the back workouts.
When you are doing back workouts to increase strength, aim to do 2-6 sets of 3-5 reps per exercise, using at least 85% of your one-repetition maximum (1RM)
For a hypertrophy (muscle growth) back workout, try to perform 3-4 sets of each barbell exercise using loads that are 70 to 85% of your 1RM for 8 to 12 reps.
Know About Back Muscle
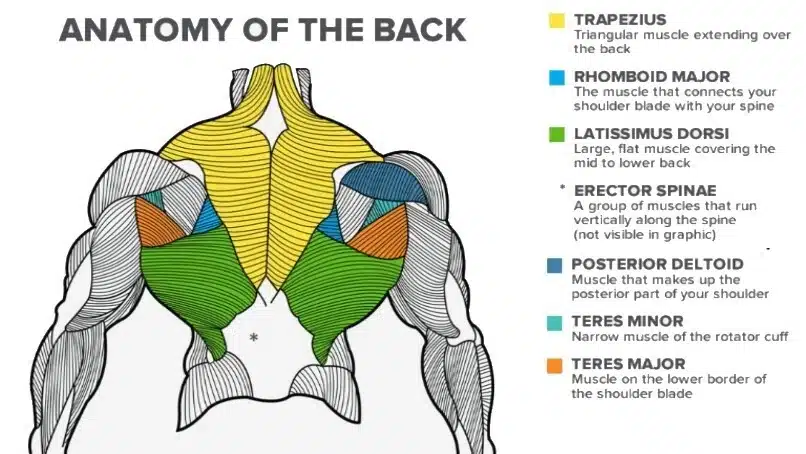
To build a strong and muscular back, you must first understand the anatomy and functionality of the back muscles. Your back muscles start just under your skull and go down to your lower back, just above your hips. These muscles connect to your ribs, vertebrae, shoulder blades, and neck.
Your back is made up of three groups of muscles. They are:
Superficial Muscles
These muscles are closer to the surface of the skin and make up the upper and lower back muscles. Includes:
- Latissimus dorsi (lats): Commonly referred to as the “lats,” large muscles that extend from the middle and lower back to the armpits
- Rhomboids: Located between the shoulder blades. They run from the medial border of the scapula (shoulder blade) to the spine.
- Trapezius (traps): Large, triangular muscle that extends from the base of the skull down to the mid-back.
- Levator scapulae: Located on the side and back of the neck. It runs from the upper cervical vertebrae to the upper border of the scapula (shoulder blade)
Intermediate Muscles
This group comprises the serratus posterior inferior and serratus posterior superior, which are situated in the shoulder girdle, between the shoulder blades.
Intrinsic Muscles
Found deep beneath the skin, the intrinsic muscles consist of two groups:
- Erector spinae: The erector spinae is a group of muscles that run alongside the spine
- Transversospinalis: They consist of several smaller muscles that run obliquely, crossing multiple vertebral levels.
The back consists of several layers of muscle, stacked like a sandwich. The muscles of the back subdivide into three categories.
12 Best Back Exercises To Build Bigger Back
The back exercises are divided into barbell rowing, dumbbell rowing, pullover, cable and machine and body-weight exercises.
- Lat Pulldown
- Barbell Shrug
- Pull-Up
- Barbell Upright Row
- Deadlift
- Bent Over Barbell Rows
- Lumbar Hyperextension
- Seated Cable Rows
- One Arm Dumbbell Rows
- T Bar Rows
- Dumbbell Pullover
- Straight Arm Lat Pulldown
- Bonus: Chin Up
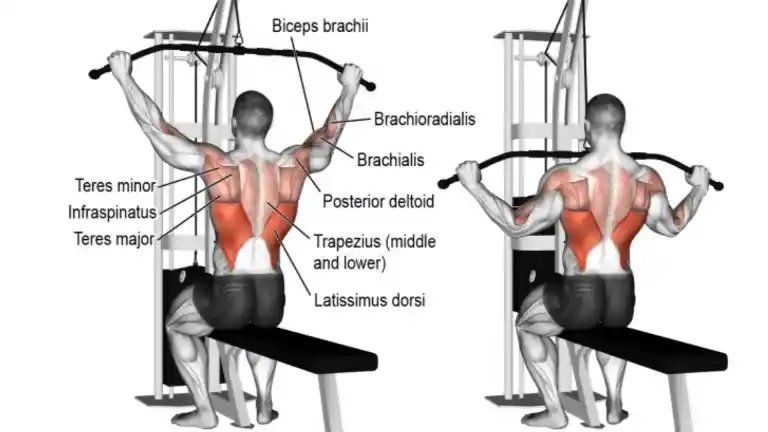
1. Lat Pulldown
The lat pulldown is an exercise used to build the muscles of the back. It is a great exercise that is widely used by fitness trainers to build bigger lats.
This isolating exercise specifically focuses on the back muscles without tiring out the biceps or triceps.
It’s important to target your back muscles to help with proper posture and to ease pulling movements.
This exercise can be performed using wide grips and narrow grips, as well as pulling to the front and the back. The wider grip is the best variation to target the outer lats.
Lat pull-down variations for back growth:
- Overhand grip pull-down
- Underhand grip pull-down
- V Bar pull-down
- Rope handle pull-down
- Single arm pull-down
How To Do It
- Take an overhand grip, hands slightly wider than shoulder-width apart, and sit on the machine seat.
- Lock your knees under the support pads.
- Keep your upper back straight, pull the bar down and bring it up to your chest.
- As you pull down, squeeze your shoulder blades together and feel back muscles contracting.
- Perform this movement using your upper lats and use the arms merely as a lever between bar and lats.
- Now release the bar with controlled motion and stretch your lats as much as possible.
Tips
- To make the most of this move, your reps should be slow and controlled.
- Go full range of motion and concentrate on your back muscles doing the major work.
- Avoid rising yourself from the seat.
Related Post: 20 Best Cable Back Exercises For Wider And Strong Back
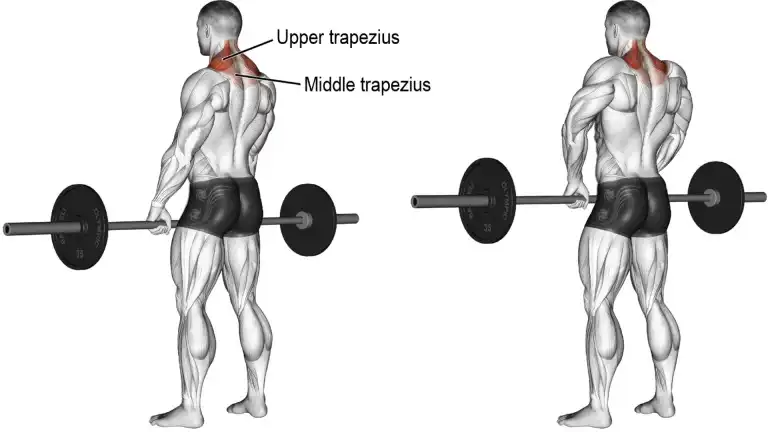
2. Barbell Shrug
The Barbell shrug is one of the best exercises to build bigger, stronger trapezius muscles. This exercise can be done extremely heavily to thicken the traps, which really helps you in doing back poses.
The Barbell Shrug is one of the best isolation exercises for the trapezius muscle. The shrug is one of the most simplistic and easy exercises to perform.
You can do the shrug either using a dumbbell, barbell, and smith machine, But the barbell variation is the classic variation to build massive traps. Traps, being a stubborn muscle group for many, can be trained with a fairly high frequency during the week.
For upper back growth and to increase the variety of your shrug exercise, you could try to :
How To Do It
- Stand with feet placed shoulder-width apart, knee slightly bent, and core stable.
- Grip the barbell with your hands facing downwards, in a pronated grip.
- Raise your shoulders without bending the elbows as far as possible, getting them closer to your ears.
- Hold the contraction and squeeze for a brief second, In a controlled and stable manner, lower the weight back down to the starting position.
Tips
- Go as high as possible, but limit momentum and excessive jerking or bouncing of the weight.
- Go full range. Move only the shoulders and keep the rest of the body steady.
Know More: 10 Best Barbell Back Exercises For Strength And Mass
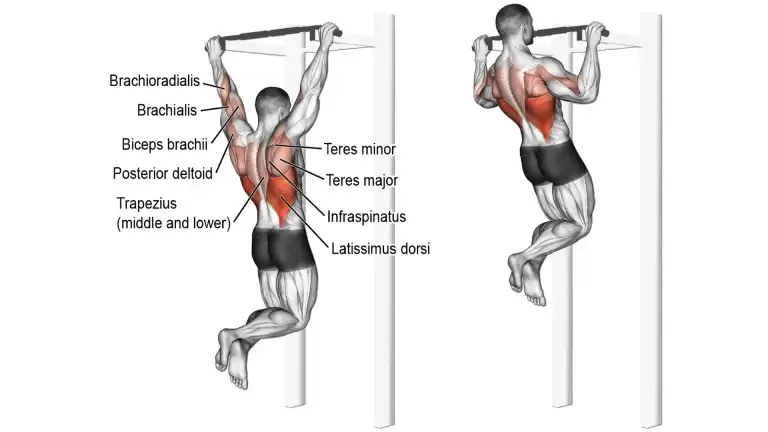
3. Pull-Up
The pull-up is an upper-body strength movement that targets your back, shoulders, and arms. Performing a pull-up is often a challenge for beginners and even experienced athletes.
The pull-up is harder to perform than a standard pull-up because your hands will be further away from the center of your body, which makes the exercise more difficult.
The pull-up increases the strength, thickness, and width of your back, specifically your lats. The lats are what influences back width and form the “V” in the upper back.
There are many variations of pull-ups that can be done to target the back:
- Wide grip pull-ups (overhand grip)
- Chin-ups (underhand grip)
- Neutral grip pull-ups (palms facing inward)
- Weighted pull-ups
- Machine assisted pull-ups
- Spotter assisted pull-ups
How To Do It
- Using an overhand grip, grab on to a pull-up bar with your hands spaced wider than shoulder-width apart.
- Hang from the bar with your arms fully extended and your chest high, while exaggerating the arch in your lower back.
- Pull yourself up by squeezing your shoulder blades together and contracting your lats until your chin passes the bar.
- Hold the contraction at the top for a second before slowly lowering yourself back to the starting position.
Tips
- To decrease bicep involvement, use a thumbless grip.
- Go full range of motion and keep form correct. Avoid jerky movements and keep them controlled.
4. Barbell Upright Row
Upright Barbell Row is an excellent exercise to build huge Trapezius muscles and create that delto-pectoral separation.
Heavy Upright Row along with shrugs build massive traps. You can use either a smith machine, free weights, or Cable to perform Upright Rows.
The upright row can be done with normal, narrow, or wider grips.
- The normal grip upright row provides overall shoulder development and is suitable for those seeking balanced muscle activation.
- The narrow grip upright rows places emphasis more on the upper trap and a little lesser on the lateral delt and rear delt.
- The wide-grip upright row places heavy emphasis more in the lateral and rear deltoid and little lessor on the upper and middle trap
Upright Row variations for back growth:
- Dumbbell Upright Row
- Upright Cable Row
- Kettlebell Upright Row
- Rope Upright Row
- Ez Bar Upright Row
- Smith Machine Upright Row
- Single Arm Upright Row
- Resistance Band Upright Row
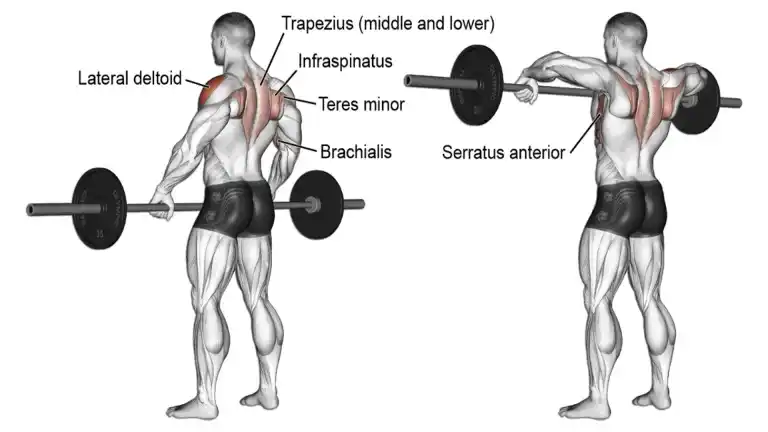
How To Do It
- Hold a bar with a narrow overhand grip and let it hang in front of you.
- Lift the bar and get it as close as possible to the chin, using your arms and elevating your shoulders to squeeze your trapezius muscles.
- Now lower the bar under controlled motion until it comes back to its starting position.
- Repeat for desired reps.
Tips
- Focus on keeping your elbows higher than your forearms
- Keep a controlled motion and avoid jerky movements.
- Keep your back straight.
5. Deadlift
The deadlift is the King of all exercises. This power exercise is designed to build an overall physique that utilizes more muscles than any other exercise. The deadlift is the best exercise for posterior chain muscle strengthening. It works your whole body including the Lower back, upper back, arms, legs, and buttocks.
It is the biggest muscle builder, recruiting more muscle motor units than any other exercise. This exercise can be performed using either a barbell or a pair of dumbbells.
You can go real heavy on a barbell deadlift, but do this exercise with caution and technique.
Deadlift variations for back growth:
- Dumbbell Deadlift
- Cable Deadlift
- Barbell rack pull
- Romanian deadlift
- One Leg Dumbbell Romanian Deadlifts
- Landmine Deadlift
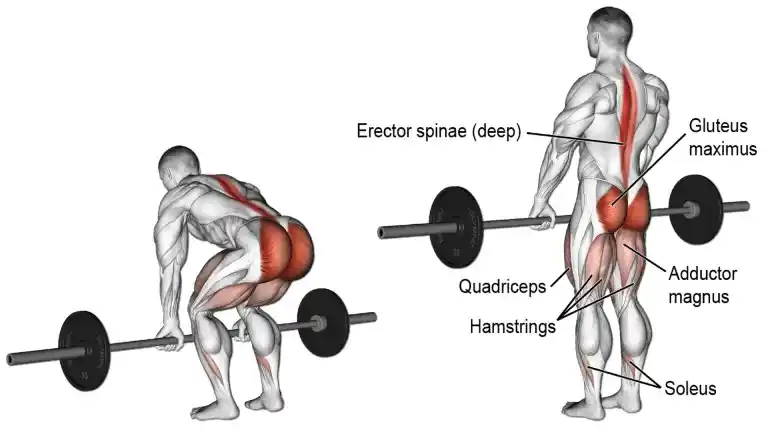
How To Do It
- Place a barbell loaded with weights in front of you.
- Grab the barbell using an underhand grip with one hand and an overhand grip with the other hand.
- Remember to keep your back as straight as possible and contract your back and hamstrings.
- Now raise the bar from the ground using your hamstrings and glutes.
- You should keep your legs slightly bent, back straight and head looking up. The initial movement is to be provided by your heels and not toes or elbows.
- Raise it to the point where your body is erect. Do not hyperextend your body as the weight shifts to the lumbar spine.
- Hold the bar for a moment at the top of the lift and remember to lockouts.
- Complete the lift and do not go only halfway through.
- Now lower the bar slowly at a steady slow pace by bending at the hips first and then at the knees and let the weight touch the ground for a moment before you begin the next rep
Tips
- If you’re going heavy (sets of fewer than about 6 reps), do deadlifts first, so you’re fresh. If you’re doing for repetitions, you can do them later in your workout.
- If performed deadlift incorrectly, it can cause more harm than good. Keep the back straight at all costs.
- Lower back muscles take along to recuperate and hence once a week heavy deadlifts will do the job.
- Go full range of motion and keep form correct. Avoid jerky movements and keep them controlled.
6. Bent Over Barbell Rows
If you are looking to strengthen your complete back: upper back, lower back, lats, traps, spinal erectors, then bent over barbell rows are the best exercise. And the science backs it up.
Spacing your hands shoulder-width apart or closer targets the central inner section of the lats, whereas a wider grip targets the outer lats.
Pulling the bar up higher toward the chest targets the upper latissimus and trapezius. Pulling the bar through a lower trajectory to touch the abdomen targets the lower lats.
Bent-over row variations for back growth:
- Overhand grip bent-over rows
- Underhand grip bent-over rows
- Pendlay rows
- Dumbbell Bent Over dumbbell Row
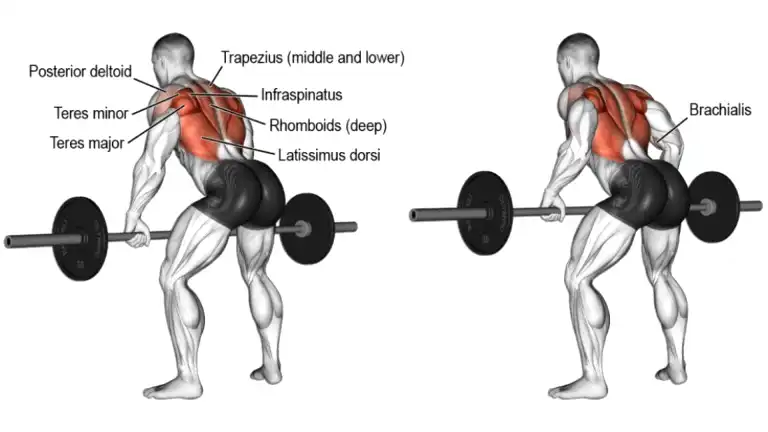
How To Do It
- Stand with a narrow stance and grab a bar with an overhand grip.
- Bend your torso forward at an angle of 45 degrees to the floor with the knees slightly, and let the bar hang in front of you.
- Now use the back and raise the bar until it touches the abdominal region and not the chest region, as it reduces back muscle contraction.
- Slowly lower the bar under control to the starting position.
Tips
- Do not use more weight than you can handle. This fatigues your spinal erectors and says goodbye to form.
- Exhale on pushing movement, and inhale when returning to the starting position.
- Hold a neutral spine throughout the movement to prevent injury.
7. Lumbar Hyperextension
Hyperextension exercise directly hits the erector spinae muscles, building a strong back. It helps to build the lower back Erector spinae muscles. This exercise is done on a hyperextension Bench/Roman Chair. Making
Hyperextensions difficult, you can also hold a plate to your chest or behind the head for additional resistance if the exercise becomes easy, and you can do a lot of reps.
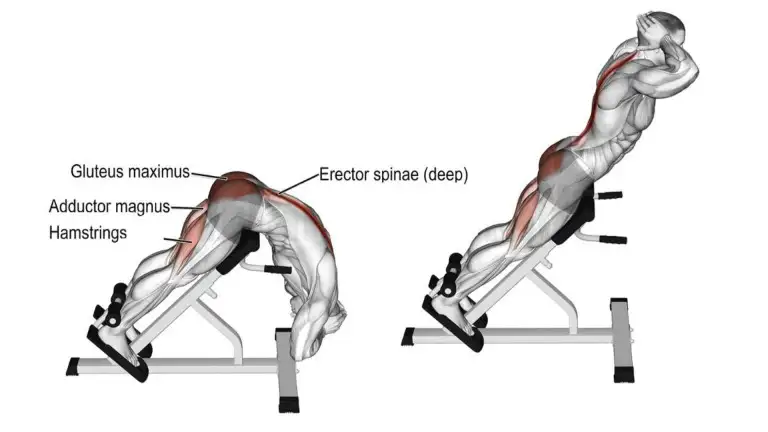
How To Do It
- Lie face down on a Hyperextension bench and hook your legs under support. Let your body be parallel to the ground.
- Place your hands on your chest (or behind your neck) and bend down through your waist until you reach a 90-degree bend.
- Return to the start position, but avoid extending beyond the body level.
- Do the desired number of reps and sets.
Tips
- Avoid hyperextension beyond the body level.
- Keep movement always under control, without letting gravity take you down faster.
8. Seated Cable Rows
Seated Cable Rows is an excellent exercise to build middle back muscles and this works on lower lats as well. It can be done with wide and narrow grips. This exercise is done on a cable rowing machine with separate handles.
In contrast to other free-weight variations, the classic seated row maintains constant tension throughout the movement.
The cable row training offers almost unmatched versatility because you can change up the load, angle, grip positioning and body positioning easily.
This back exercise is done on a cable rowing machine with separate handles and grip position change, the muscle worked involvement.
- Pronated (overhand) grip tends to target the upper and middle trapezius.
- Neutral (thumbs up) grip hits the middle and lower trapezius.
- Supinated (underhand) grip switches the focus to the latissimus dorsi.
Different attachments can be used for back growth.
- Wide Grip Seated Row
- Single-arm row
- Rope attachment
- Long bar….. Get creative!
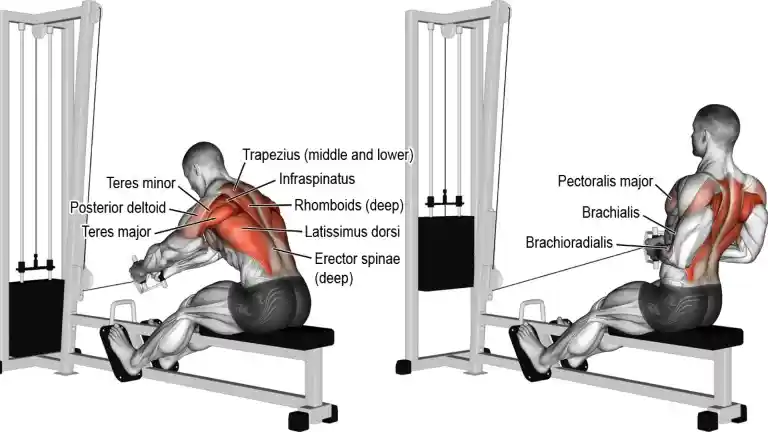
How To Do It
- Sit on a seated cable pulley rowing machine with legs slightly bent and feet supported against the crossbar.
- Take hold of the handles with your arms extended and back stretched.
- Pull the handles so that they come as close to the lower chest/abdomen as possible.
- Thrust your chest out while pulling with your body in an upright position. Slowly return the handle to the starting position.
Tips
- Pause briefly when the handles are close to the chest and squeeze your upper back muscles, bringing the scapulae closer.
- Keep your knees slightly bent to avoid knee and lower back pressure.
- Remember, a rounded back is a wrong back. Keep it straight at all times.
- Keep your upper back stationary, don’t move your upper back, back, and forth.
- These are best done toward the end of your workout, so don’t be afraid to go slightly higher-rep here, like 10-12 or even 12-15 reps
9. One Arm Dumbbell Rows
One Arm Dumbbell Rows are an excellent alternative to barbell rows, and it provides the full-range motion to build the lats muscles.
This exercise helps to work on each side independently, thereby providing better muscle isolation and a longer range of motion. This exercise is done with a heavy dumbbell with your body supported by a bench.
One arm dumbbell row variations for back growth:
- One arm row with one hand on a rack and both leg on the floor
- One arm row with one hand and one leg on a bench
- Single-arm landmine row
- Single arm meadows row
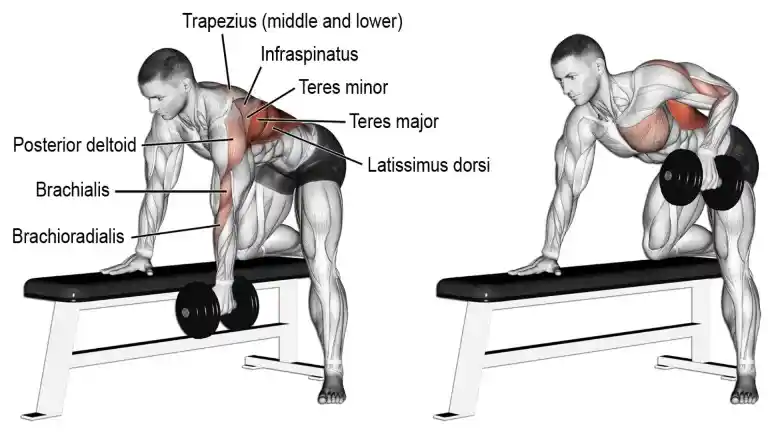
How To Do It
- Grasp a dumbbell with palm facing in. Rest the opposite hand and knee on a bench, keeping your spine straight and just above parallel to the floor.
- Pull the dumbbell vertically upward alongside your torso, raising the elbow as high as possible.
- Slowly lower the dumbbell as low as possible feeling a good lats spread.
- Repeat on the other side.
Tips
- Keep motion under strict control for better isolation.
- Avoid hunchback bending as it leads to Injury.
10. T Bar Rows
T bar Row is a power exercise to build middle back muscles. Check the correct execution technique and blast your back muscles. It also works on the outer lats when done with a narrower grip.
It is done on a T bar machine or placing a barbell at the corner. T bar rows are a tough exercise, but building a strong back is a must to develop a quality physique, stay injury-free, and back pain-free for life.
The chest supported row exercise is similar to the T bar row and allows you to concentrate on working, the vast majority of muscles located on the posterior side of the upper body.
This variation of the row requires less effort to keep your body stable because one end of the bar pivots at a fixed point on the floor and the chest supported on the bench.
Chest-supported row variations to grow the bigger and stronger back:
- Dumbbell Chest Supported Row (Underhand, Overhand, Single hand and Neutral grip)
- Barbell Chest Supported Row (Underhand, Overhand)
- Chest Supported Row with Cables. (Underhand, Overhand, Single hand and Neutral grip)
- Machine Chest Supported Row. (Underhand, Overhand and single Arm)
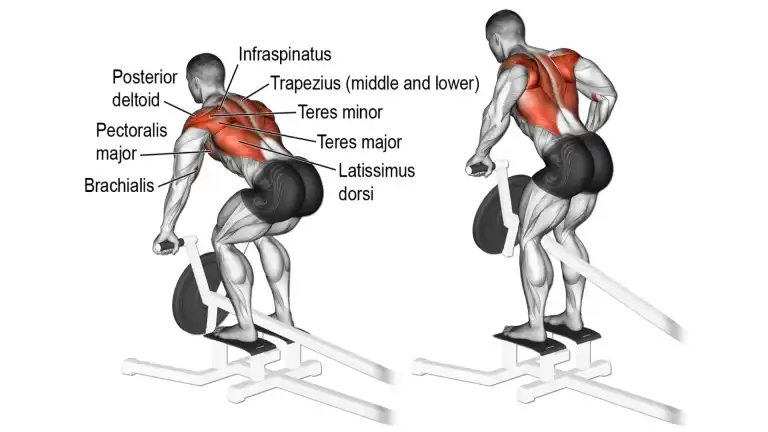
How To Do It
- Standing on a T bar machine, grab its handles with an overhand grip.
- Keep your feet a bit apart and knees slightly bent.
- Bend at the hips and keep your back arched throughout the movement.
- Lift the bar until the bar touches your chest, keeping the back straight.
- Now slowly lower the bar until it nearly touches the ground.
Tips
- Exhale while you exert.
- Avoid hunchback bending as it leads to Injury.
- Go Complete range of motion.
11. Dumbbell Pullover
Dumbbell Pullover is the best exercise to build a strong rib cage and build serratus anterior muscle to build a complete chest and back.
Pullover work directly on the serratus anterior muscle to develop the back. This exercise is done lying across a bench with a heavy dumbbell.
The best Pull over exercise variations to train your back.
- Flat bench pull-over (dumbbell, barbell, weight plate)
- Incline pull-over (dumbbell, barbell, weight plate)
- Decline pull-over (dumbbell, barbell, weight plate)
- Cable pull-over
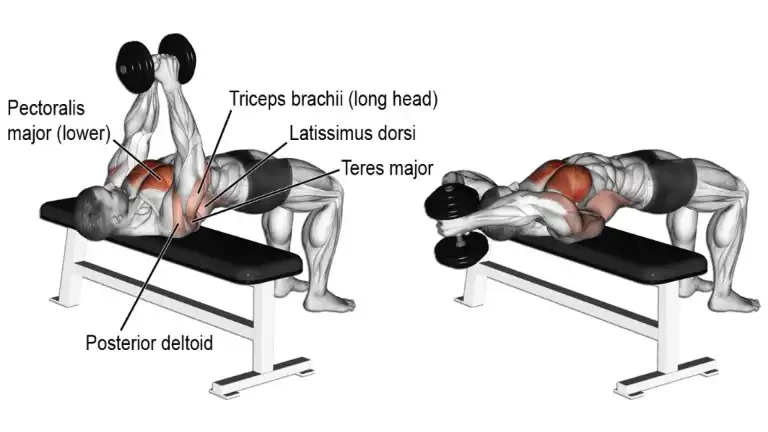
How To Do It
- Lie across on a bench on your shoulders so that your head is hanging.
- Grasp a dumbbell with both hands and get it straight over your chest.
- Lower the dumbbell in an arc slowly, getting a good stretch in your rib cage.
- Lower the dumbbell as far as possible and then raise it back to the starting position.
Tips
- Exhale while you exert.
- Maximum stretching ensures the greatest expansion of the rib cage.
- Relax your hips and let them fall, as relaxed hips help in extra expansion.
12. Straight Arm Lat Pulldown
The straight arm pulldown is one of the best exercises for strengthening your lats. This isolation exercise can also help improve your posture and build a stronger back.
The straight-arm pulldown trains the lats through a long range of motion, and is helpful for people who have trouble feeling their backs work on conventional pulldown exercises. As a result, it’s a great movement for focusing on lat development.
While the exercise will primarily target the lats, you will also notice a fair amount of bicep and middle back activation.
Straight Arm Lat Pull Down variations for back growth:
- Wide grip Straight Arm Lat Pulldown
- Close grip Straight Arm Lat Pulldown
- Rope straight Arm Lat Pulldown
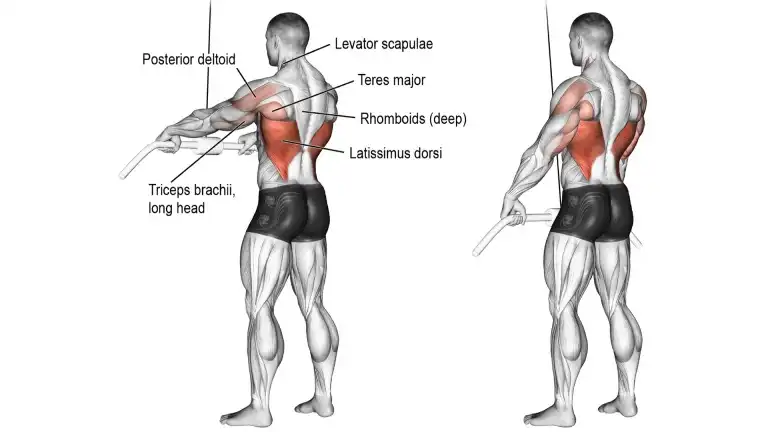
How To Do It
- Take an overhand grip that is wider than shoulder-width on a lat bar attached to the pulley on the lat pulldown bar.
- Position yourself with your feet flat on the floor, chest up, and low-back arch exaggerated.
- Pull your shoulder blades together as you squeeze your lats to initiate the movement, pulling the bar down in a smooth motion to your midsection.
- Hold the contraction for a moment, then slowly return the bar all the way back to the starting position.
Tips
- Don’t allow the head to jut forward as you pull.
- Keep your elbows slightly flexed and your body still
Bonus: Chin Up
A chin-up is a strength training exercise that uses your entire body weight, with a special focus on your upper body and core. Chin-ups are the best exercise to build sweeping upper lats. This is a bodyweight exercise that can induce serious muscle growth of the back and biceps.
In this exercise, the palms are faced towards the body. Since the lifter is pulling their own bodyweight, the biceps are usually exposed to loads heavier than what one can lift with a barbell.
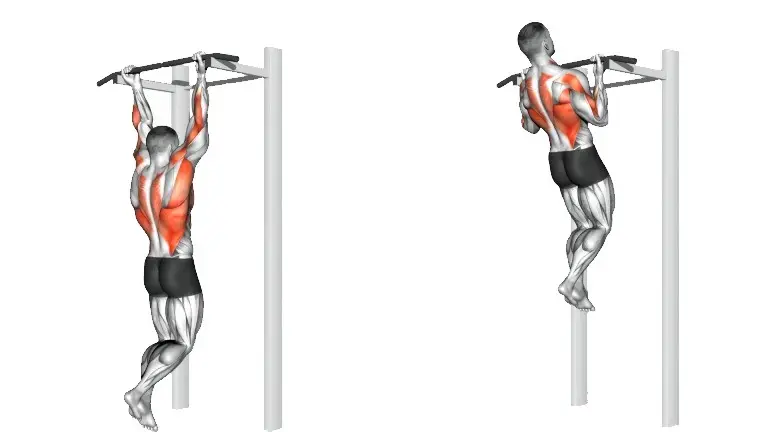

How To Do It
- Grab a pull-up bar with an underhand grip (palm facing toward the body), hands shoulder-width apart or slightly narrower.
- Straighten your arms, keep your knees bent and cross your lower legs. It can also be done with leg straight.
- Retract your shoulder blades and pull your body until your chin becomes aligned with the bar.
- Pause for one to two seconds at the top, with the biceps under maximum tension. Slowly lower to the start position.
Tips
- Don’t get in the habit of doing half reps and chasing numbers.
- Lower to almost full extension of the elbow, but avoid locking out completely.
Complete Back Workout To Build Mass
Effective back training should incorporate a variety of exercises and target all the majors back muscles.
For a complete back workout and to build balanced strength, you’ll need to make sure you’re doing a variety of back exercises to specifically target your upper, middle and lower back muscles.
Upper and middle back exercises target the trapezius and lats.
When choosing exercises for your upper back, you should include a variety of high pulling exercises, such as rows and straight arm lat pull down.
The lower back can be targeted with exercises like deadlift and seated cable rows.
This training routine for the back is designed to increase strength and muscle mass. However, the gains will be increased with the use of primary lifts like deadlift, Bent-Over Row.
Sets and Reps For Back Workout
Of course, the number of sets and reps will be determined based on your fitness journey, but here is a great starting point:
Sets
- Beginners: ~10 sets per week.
- Intermediate: ~15 sets per week.
- Advanced: ~20 sets per week.
When a certain amount of volume stops being effective and your progress stalls, you can add sets to increase volume and use that as a driver of renewed progress.
Reps
The best rep ranges and loads to work with.
- 6-8 reps with heavy load
- 8-15 reps with moderate load
- 15-20+ with light load
The load should bring you to or near failure within the given rep ranges to be effective.
Back Training Plan As Per Your Goal
- For muscle endurance: Aim for 3–4 sets of 12–15 reps, with a moderate amount of resistance.
- For muscle strength: Aim for 3–5 sets of 6–10 reps, with a heavier amount of resistance.
- For muscle hypertrophy (increased muscle size): Aim for 3–4 sets of 8–12 reps, with a moderate to heavy amount of resistance.
It is always best to start with a lower number of reps and sets, and then gradually increase as your strength improves. Furthermore, it is important to allow for adequate rest between sets, typically 60–90 seconds.
Strength, Power, Hypertrophy and Endurance table of Mell Siff’s Supertraining
| Variable | Strength | Power | Hypertrophy | Endurance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Load (% of 1RM) | 80-90 | 45-55 | 60-80 | 40-60 |
| Reps per set | 1-5 | 1-5 | 6-12 | 15-60 |
| Sets per exercise | 4-7 | 3-5 | 4-8 | 2-4 |
| Rest between sets (mins) | 2-6 | 2-6 | 2-5 | 1-2 |
| Duration (seconds per set) | 5-10 | 4-8 | 20-60 | 80-150 |
| Speed per rep (% of max) | 60-100 | 90-100 | 60-90 | 60-80 |
| Training sessions per week | 3-6 | 3-6 | 5-7 | 8-14 |
Back Exercises Workout Samples
Beginner Back Workout Plan
If you’re new to lifting weights, don’t worry. This beginner-friendly back workout routine is a great place to start.
When this becomes easier, you should pick a heavier weight.
After you’ve upped your weight several times and feel strong in the movements below, move on to the intermediate routine. Until then, you can follow this beginner back workout plan.
- Pull Ups: 4 sets of 10-15 reps.
- Seated Cable Row: 4 sets of 10-15 reps.
- Bent Over Dumbbell Rows: 3 sets of 15-10 reps.
Intermediate Back Workout
If you are an intermediate level or have outgrown the beginner routine, try the intermediate back workout routine below.
Regardless of how many reps your programming is calling for, you should be unable to complete the last one with proper form.
- Deadlift: 4 sets of 6-8 reps.
- One Arm Dumbbell Rows : 3 sets of 8-10 reps.
- Lat Pull Down: 4 sets of 10-12 reps
- Dumbbell Pullover: 3 sets of 8-10 reps.
Advanced Back Workout
If you are an advanced level athlete or have already completed the beginner and intermediate back workouts, give the advanced routine a try.
Here, you’ll challenge more of your balance, stability, and strength
- Barbell Deadlift: 3 sets of 8-12 reps.
- Barbell Bent Over Row: 4 sets of 6-8 reps.
- T Bar Rows: 4 sets of 8-10 reps.
- Barbell Upright Row: 3 sets of 10-12 reps.
FAQ About Back Training
To conclude, let’s go over some frequently asked questions about training your back
What is the king of all back exercises?
The deadlift is the king of all back exercises. It is a compound movement that targets multiple muscles in the back, including the erector spinae, latissimus dorsi, and trapezius. Deadlifts are highly effective for building overall back strength, improving posture, and improving functional fitness.
Can I do back exercises everyday?
No, it is generally not recommended to perform back exercises every day. Like any muscle group, the back muscles need time to recover and grow. Allow at least 48 hours of recovery time between intense back workouts.
How To Train Upper, Middle and Lower Back
As you saw above, many exercises engage both primary and secondary muscles.
In order to build an all-around strong back, we will need to hit all areas.
- For the lower back, you can do exercises like deadlifts to strengthen the posterior chain.
- For middle back, focus on exercises where your hands are closer together, like close-grip rows.
- The upper back, can be done with exercises like Pull-ups, single-arm bent over rows and upright row.
- The Trap muscles can be done with exercises like shrug and upright row.
Conclusion
This exercise is highly recommended for anyone interested in building back strength and gaining muscle size.
It not only allows for targeted muscle development, but also provides an overall upper body workout.
Be smart: don’t limit yourself to one type of equipment for back training. Get the benefits of a full back workout using different equipment.
- Cable Back Exercises
- Barbell Back Exercises
- Dumbbell Back Exercises And Workout
- Bodyweight Back exercises
If you do these back exercises consistently, the results will speak for themselves.
Thanks for reading, enjoy working your Back Workout!
References
- Schoenfeld, Brad MSc, CSCS; Kolber, Morey J PT, PhD, CSCS; Haimes, Jonathan E BS, CSCS: The Upright Row: Implications for Preventing Subacromial Impingement. Strength and Conditioning Journal: October 2011 – Volume 33 – Issue 5 – p 25-28
- Cools AM, Witvrouw EE, Declercq GA, Danneels LA, Cambier DC. Scapular muscle recruitment patterns: Trapezius muscle latency with and without impingement symptoms. Am J Sports Med 31: 542–549, 2003.
- Int J Environ Res Public Health. Trapezius muscle timing during selected shoulder rehabilitation exercises. 2021 Jun 14;18(12):6444. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18126444.PMID: 34198674
- Lorenzetti S, Dayer R, Pluss M, List R. Pulling exercises for strength training and rehabilitation: movements and loading conditions. J Funct Morphol Kinesiol. 2017;2(3):33. doi:10.3390/jfmk2030033
- Chad M J Fenwick, Stephen H M Brown, Stuart M McGill. Comparison of different rowing exercises: trunk muscle activation and lumbar spine motion, load, and stiffness. PMID: 19620925 DOI: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e3181b07334
- Jett, David Michael Jr. M.S., C.S.C.S., EP-C, PN; Gibb, Jessica M.S., CEP, EP-C, FMSC; Verrill, David E. M.S., RCEP, CEP, PD, FAACVPR. Evidence-based Alternatives To Popular Exercises. ACSM’s Health & Fitness Journal: November/December 2017 – Volume 21 – Issue 6 – p 20-26
Best Barbell Back Exercises For Mass And Stronger

Manish brings over 10 years of hands-on experience in weight lifting and fat loss to fitness coaching. He specializes in gym-based training and has a lot of knowledge about exercise, lifting technique, biomechanics, and more.
Through “Fit Life Regime,” he generously shares the insights he’s gained over a decade in the field. His goal is to equip others with the knowledge to start their own fitness journey.
